Imagine waking up one morning with swelling in parts of your body, face, hands, or feet. It’s a situation that might seem like a strange dream, but for those dealing with Angioedema, it can be a reality they face. Understanding Angioedema—what it is, why it occurs, how it’s diagnosed, and the options for managing it—is crucial for those living with the condition and their loved ones.
Angioedema, a relatively lesser-known condition, can disrupt daily life. But by shedding light on this condition, we can empower those affected by it and cultivate empathy and understanding among those who are not. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify Angioedema, breaking it down from its causes to its treatment, providing a beacon of knowledge in what can often feel like uncharted waters.
So, this guide is for you, whether you’re someone dealing with Angioedema or simply an individual looking to expand your knowledge. So, let’s pull back the curtain and dive into the world of Angioedema, one topic at a time.
What is Angioedema?
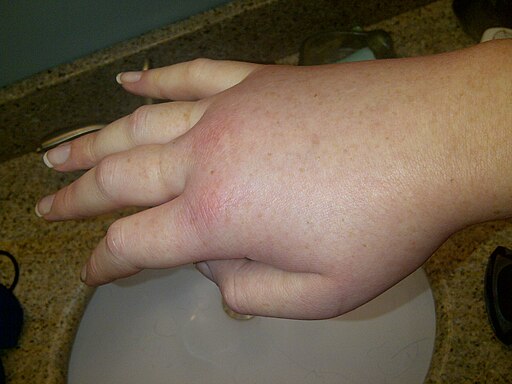
Angioedema – it’s a word that might not roll off the tongue easily. Still, it’s an important term, especially for those with this condition. But what exactly is Angioedema?
In simple terms, Angioedema is a swelling beneath the skin, usually in the face, hands, feet, or genitals. It’s similar to hives, but while hives affect the skin’s surface, Angioedema affects the deeper layers. This swelling can occur suddenly and unexpectedly, often as an allergic reaction, but sometimes due to other causes that we’ll discuss later.
Angioedema is categorized into different types, each with its unique characteristics.
Allergic Angioedema
This type is probably the most well-known and is usually caused by an allergic reaction to something, whether it’s food, medication, or an insect bite. It’s often accompanied by other allergic symptoms like hives.
Drug-Induced Angioedema
Certain medications, like ACE inhibitors used to control blood pressure, can cause Angioedema in some people.
Hereditary Angioedema
This is a rare, inherited condition, usually triggered by stress, injury, or medical procedures. Unlike allergic or drug-induced Angioedema, hereditary Angioedema doesn’t typically come with hives. It can lead to recurrent episodes of swelling.
Idiopathic Angioedema
When the cause of Angioedema isn’t clear, it’s referred to as idiopathic. It’s often challenging to manage because the triggers aren’t easily identifiable.
So, there you have it—the basics of what Angioedema is and the different forms it can take. Understanding these nuances is key to managing this condition and navigating the journey toward better health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Angioedema

Now that we’ve covered what Angioedema is let’s delve into the why. What causes this sudden, beneath-the-skin swelling? Like many health conditions, the causes can be quite diverse, often varying based on the type of Angioedema.
Allergic Angioedema is typically triggered by an allergic reaction. Common culprits include certain foods (such as peanuts, shellfish, or eggs), medications (like penicillin or aspirin), insect bites or stings, or even exposure to certain environmental factors like pollen or animal dander. The body, reacting to what it perceives as a threat, releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream, causing swelling.
Drug-Induced Angioedema is a result of a reaction to specific medications. One of the most common groups of drugs that can cause this type of Angioedema is ACE inhibitors, which are used to treat conditions like hypertension and heart disease.
Hereditary Angioedema, as the name suggests, is a condition that runs in families. It’s caused by a mutation in one gene affecting blood proteins. People with this form of Angioedema experience recurrent episodes of swelling without the typical hives accompanying allergic reactions. Instead, triggers often include stress, minor trauma, surgery, or illnesses.
Idiopathic Angioedema is a bit of a mystery. It’s when the swelling occurs without a clear cause. It can be frustrating to deal with because, without identifiable triggers, managing it becomes more complex.
When it comes to risk factors, anyone can develop Angioedema. However, you may be more at risk if you have a personal or family history of allergies or allergic reactions, or undergoing certain medical treatments. For Hereditary Angioedema, having a family history of the condition is the primary risk factor.
While Angioedema can be scary and unsettling, understanding its causes and risk factors is the first step in managing it effectively. Remember, each person is unique, and what triggers an episode in one person might not be in another. However, keeping track of potential triggers can help manage this condition.
Symptoms and Complications of Angioedema

Recognizing the symptoms of Angioedema is crucial for timely treatment and management. Symptoms can differ based on the type of Angioedema, but let’s discuss the common ones first.
Most often, Angioedema presents as sudden, intense swelling beneath the skin. This swelling can occur in various body parts but is most commonly seen in the face, lips, eyes, hands, feet, and genitals. In some cases, the swelling can also affect the lining of the throat, tongue, or lungs, leading to difficulty breathing, which can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Other potential symptoms include redness around the swelling, a sensation of heat or pain at the swollen site, and the appearance of hives in the case of allergic or drug-induced Angioedema.
In Hereditary Angioedema, the swelling may last longer (up to a few days) and occur without hives. Abdominal pain caused by swelling in the stomach lining is also a common symptom in this form of Angioedema.
Now, let’s talk about complications. The most serious complication associated with Angioedema is difficulty breathing due to swelling in the throat or tongue. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Another potential complication, specifically in Hereditary Angioedema, is severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting due to swelling in the stomach lining. This can often be mistaken for conditions like appendicitis or a stomach ulcer.
Remember, Angioedema can vary greatly from person to person. If you suspect you or someone else is experiencing Angioedema, especially if there’s difficulty breathing, seek medical help immediately. Understanding the symptoms and potential complications can save lives and ensure better management of this condition.
Diagnosis of Angioedema
Understanding symptoms is one thing, but how does a healthcare professional diagnose Angioedema? Let’s walk through the diagnostic process.
The first step in diagnosing Angioedema often involves thoroughly discussing your symptoms, medical history, and potential exposure to allergens or triggers. Your doctor will want to know when the swelling began, how long it lasts if anything seems to trigger it, and if you have a family history of similar symptoms or have been diagnosed with Angioedema.
A physical examination usually follows this discussion. Your doctor will check for areas of swelling and hives and may also perform a general examination to rule out other potential causes for your symptoms.
Further tests may be required in some cases, especially when Hereditary Angioedema is suspected. These can include blood tests to check levels of certain proteins in your blood or genetic tests to look for mutations associated with Hereditary Angioedema.
Allergic and Drug-induced Angioedema may require specific allergy tests or medication reviews to identify potential triggers. For Idiopathic Angioedema, where the cause isn’t clear, the diagnostic process might involve eliminating and ruling out potential causes until the doctor arrives at a diagnosis.
It’s important to note that diagnosing Angioedema can sometimes be a complex process, particularly when the cause isn’t immediately apparent. Patience and open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial during this process. Remember, an accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment and management.
Treatment Options for Angioedema
With a clearer understanding of Angioedema, its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic process, we now arrive at a crucial topic: treatment. The treatment for Angioedema largely depends on the type and severity of the condition. Let’s explore some of the common options.
Allergic and Drug-Induced Angioedema are often treated initially with antihistamines, which can help control the swelling and itching. Avoidance is key if a specific allergen or medication is identified as the trigger. In severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation. For life-threatening episodes, an injection of epinephrine can be life-saving.
Treatment for Hereditary Angioedema focuses on preventing and managing episodes. Medications to regulate blood proteins may be prescribed, and some medications can help control swelling for acute attacks. People with Hereditary Angioedema must avoid triggers, which often include stress, trauma, and certain medical procedures.
For Idiopathic Angioedema, treatment can be more challenging due to the unknown cause. Antihistamines and corticosteroids are often used; if these are ineffective, other medications may be tried.
Living with Angioedema
While the medical aspects of Angioedema are undeniably important, it’s equally crucial to address the day-to-day reality of living with this condition. Here, we’ll discuss some practical tips and strategies to help manage life with Angioedema.
Identifying and avoiding triggers
Keeping a symptom diary can be incredibly helpful. Jot down what you ate, what activities you did, and any other notable occurrences before an Angioedema episode. Over time, you may see patterns emerge that can help you identify and avoid triggers.
Having an emergency action plan
If your Angioedema can cause severe or life-threatening reactions, having an emergency action plan is essential. This could include having emergency medication always available, wearing a medical alert bracelet, and ensuring your friends, family, and coworkers know how to respond in an emergency.
Connecting with others
Living with a condition like Angioedema can sometimes feel isolating. Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be comforting. Look for local or online support groups where you can share experiences and learn from others.
Self-care
Dealing with Angioedema can be stressful. Engaging in regular self-care activities can help manage this stress. This might include activities like yoga, meditation, reading, gardening, or anything else that helps you relax and feel good.
Working with your healthcare team
Your doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals are there to support you. Don’t hesitate to contact them with questions, concerns, or just for reassurance. They can also provide resources and referrals to other support services as needed.
Living with Angioedema may bring challenges, but remember, you’re not alone. With knowledge, support, and proactive management, you can navigate life with Angioedema successfully.
The Future of Angioedema Research
As we draw toward the conclusion of our exploration of Angioedema, let’s take a moment to look ahead. Medical research is an ever-evolving field, and the same holds for Angioedema.
Scientists and researchers are continuously working to better understand the underlying mechanisms of Angioedema, particularly the genetic aspects of Hereditary Angioedema. In addition, new treatment options are being explored, such as targeted therapies that can more precisely control the body’s response to triggers.
Moreover, the development of novel diagnostic tools aims to make identifying triggers and diagnosing the condition faster and more accurate. The goal of these advancements is to enhance the quality of life for individuals living with Angioedema and ultimately find a cure.
While we await these exciting developments, remember that understanding your condition and working closely with your healthcare provider remains the best strategy for managing Angioedema effectively today.
Conclusion
We’ve journeyed through the world of Angioedema, understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and treatments. We’ve also explored what it’s like to live with this condition and the promising future research holds.
It’s important to remember that every individual’s experience with Angioedema is unique. While it can be a challenging condition, it can be effectively managed with the right knowledge, treatment, and support.
If you or someone you know is dealing with Angioedema, remember that medical professionals are there to help. Don’t hesitate to reach out to them for guidance and support.
Thank you for taking the time to educate yourself about Angioedema. By understanding more about this condition, we can all play a part in raising awareness, promoting research, and supporting those who live with it daily.
FAQs
What is Angioedema?
Angioedema is characterized by swelling beneath the skin’s surface, often occurring in the face, lips, eyes, hands, feet, or genitals.
What are the different types of Angioedema?
The four main types of Angioedema are Allergic Angioedema, Drug-induced Angioedema, Hereditary Angioedema, and Idiopathic Angioedema.
What causes Angioedema?
Causes vary depending on the type. Allergic and Drug-induced Angioedema is caused by an allergic reaction or a reaction to certain medications, respectively. Hereditary Angioedema is caused by a genetic mutation, while the cause of Idiopathic Angioedema is unknown.
What are the symptoms of Angioedema?
Symptoms include sudden, intense swelling beneath the skin, redness around the swelling, a sensation of heat or pain at the swollen site, and in some cases, difficulty breathing.
How serious is Angioedema? Can it be life-threatening?
While most cases of Angioedema are uncomfortable but not dangerous, swelling in the throat or tongue can be life-threatening due to the risk of asphyxiation. This requires immediate medical attention.
How is Angioedema diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a discussion of symptoms and medical history, a physical examination, and in some cases, further tests such as blood tests or allergy tests.
What are the treatment options for Angioedema?
Treatment options depend on the type and severity of Angioedema and can include antihistamines, corticosteroids, medications to regulate blood proteins, and avoidance of known triggers.
What are some strategies for living with Angioedema?
Strategies include identifying and avoiding triggers, having an emergency action plan, connecting with others through support groups, engaging in regular self-care activities, and working closely with a healthcare team.
What is the future of Angioedema research?
Future research is focused on better understanding the underlying mechanisms of Angioedema, developing new treatment options, and creating novel diagnostic tools to make identification and diagnosis faster and more accurate.
Can Angioedema be cured?
While there is currently no cure for Angioedema, it can be effectively managed with the right treatment and support. Ongoing research aims to enhance the quality of life for individuals with Angioedema and ultimately find a cure.
References
- NHS inform – angioedema
- The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) – Hives (Urticaria) and Angioedema Overview
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.