Boil is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. While not usually serious, boils can cause discomfort and frustration. Seeking the right information and knowing how to manage and treat them can make all the difference.
Understanding Boils: Causes and Symptoms
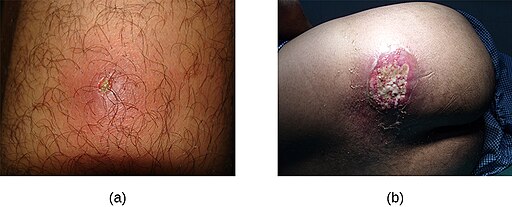
Boils, known as skin abscesses, are localized infections in hair follicles or oil glands. Bacteria, specifically Staphylococcus aureus, primarily cause boils. The bacteria enter the skin through cuts, insect bites, or hair follicles, leading to infection and a painful, pus-filled lump.
Identifying a boil is relatively straightforward. It typically starts as a tender, red bump that becomes more swollen and painful. Over time, the lump grows, forming a head filled with yellow or white pus. Additional symptoms may include increased sensitivity, warmth, and surrounding skin redness.
Types of Boils: Differentiating and Identifying
While boils generally share common characteristics, several distinct types exist, each with unique features. Understanding the differences can help in accurate identification and appropriate treatment.
- Furuncles: Furuncles, commonly called boils, are deep-seated infections of hair follicles. They appear as painful, red nodules that gradually develop into larger, pus-filled abscesses.
- Carbuncles: Carbuncles are clusters of furuncles that form deeper, larger, and interconnected abscesses. They often occur on the back of the neck, shoulders, or thighs. Carbuncles are more severe than individual boils and may cause fever and fatigue.
- Pilonidal Cysts: Pilonidal cysts are boils that form at the base of the tailbone, primarily affecting young adults. These cysts occur due to ingrown hairs or hair follicles, leading to infection and a painful abscess.
While the above boils are most common, other variants exist, such as hidradenitis suppurativa, which affects sweat glands, and Bartholin’s gland cysts, which occur in the genital area.
Prevention: Tips to Reduce the Risk of Boils
While dealing with existing boils is crucial, preventive measures are equally important to reduce the likelihood of developing new ones. Here are some key tips to help minimize the risk of boils:
- Practice good personal hygiene by regularly washing your hands with soap and water to prevent the spread of bacteria. Cleanse the affected area gently and keep it dry.
- Clean and disinfect shared items: Regularly clean and disinfect items such as towels, clothing, and bedding to prevent the transmission of bacteria. Avoid sharing personal items, especially with individuals who have existing boils.
- Avoid squeezing or picking at boils: Manipulating boils can introduce additional bacteria or worsen the infection. Let them heal naturally or seek medical assistance for drainage.
- Strengthen your immune system: Boost your immune system by incorporating a well-rounded diet filled with abundant fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Preventing boils requires adopting a proactive approach to personal hygiene and overall health:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water.
- Maintain clean and well-moisturized skin.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, and clothing.
- Keep your living environment clean and sanitized.
- Practice safe shaving techniques to avoid skin irritation.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to reduce friction and sweat buildup.
- Strengthen your immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest.
Diagnosis and Medical Treatment
Suppose you suspect you have a boil or are experiencing persistent symptoms. In that case, seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial. A healthcare professional will typically examine the affected area and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
In some cases, laboratory tests may be necessary to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection or to rule out any underlying conditions. Once diagnosed, your healthcare provider will recommend an appropriate treatment plan. Here are some common medical treatments for boils:
- Antibiotics: For mild cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection. Oral antibiotics like dicloxacillin or cephalexin are commonly used. In more severe cases or when the infection spreads, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
- Incision and drainage: In some cases, especially when the boil is large or causing severe pain, your healthcare provider may need to make a small incision to drain the pus. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, ensuring minimal discomfort.
- Steroids: In certain situations, your healthcare provider may prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and promote healing. This treatment option is usually reserved for severe or recurring boils.
- Surgical intervention: If boils are persistent or recurring, your healthcare provider may recommend surgical procedures to remove the infected hair follicles or glands, preventing future episodes. These procedures may include surgical incision and drainage, laser hair removal, or excision.
While medical treatment is essential, self-care practices can complement and enhance healing. For example, your healthcare provider may recommend at-home techniques such as warm compresses, proper wound care, and pain management strategies.
Natural Remedies for Boils
In addition to conventional treatments, natural remedies can complement the management of boils. While these remedies may not replace medical intervention, they can relieve and promote healing. However, remember that when it comes to natural remedies, it’s essential to exercise caution and seek guidance from a healthcare professional before incorporating them into your routine.
One effective natural remedy for boils is tea tree oil. With its antimicrobial properties, tea tree oil can help kill the bacteria causing the infection and reduce inflammation. Apply a few drops of diluted tea tree oil to the affected area several times daily for the best results.
Aloe vera is another soothing option for alleviating boil discomfort. In addition, its anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce redness and swelling. Extract the gel from an aloe vera leaf and apply it directly to the boil. Leave it on for a few hours before rinsing off.
Turmeric, a common spice with potent anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, can also be beneficial. Mix turmeric powder with a small amount of water to create a paste. Apply the paste to a boil and cover it with a clean cloth. Leave it on for a few hours before rinsing off.
Lastly, garlic possesses antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties that can aid in treating boils. Crush a few garlic cloves to extract the juice and apply it to the affected area. Cover with a clean bandage and leave it overnight. Repeat this process daily until the boil improves.
Complications and When to Seek Medical Attention
While most boils can be treated successfully with home remedies or medical interventions, certain complications may arise if left untreated or improperly managed. It’s crucial to be aware of these complications and know when to seek immediate medical attention. Here are some potential complications:
- Cellulitis: If the infection spreads to the surrounding skin, it can cause cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection characterized by redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Cellulitis requires prompt medical treatment to prevent further complications.
- Abscesses: Boils that are not adequately drained or treated may form deeper abscesses. Abscesses are larger collections of pus that may require more invasive medical interventions, such as surgical drainage.
- Scarring: Severe or recurrent boils, particularly in highly visible or sensitive areas, can lead to scarring.
- Systemic infection: Although rare, bacteria from a boil can enter the bloodstream and cause a systemic infection. This can lead to serious health complications and requires immediate medical attention.
Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial to prevent complications. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- The boil is larger than 2 inches in diameter.
- The pain becomes unbearable or affects your daily activities.
- The redness or swelling spreads to the surrounding area.
- You develop a fever.
- The boil only improves within a week or shows signs of worsening.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing and Preventing Boils
Taking control of your lifestyle habits can make a significant difference in managing and preventing boils. By incorporating these practical tips into your daily routine, you can promote healthier skin and reduce the occurrence of these bothersome skin problems.
Maintain a balanced diet.
Nourish your body with nutrient-packed foods, such as vibrant fruits, crisp vegetables, wholesome grains, and lean proteins. These healthy choices provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support your immune system and the health of your skin.
Stay hydrated
Remember to underestimate the power of hydration for maintaining healthy skin. Make it a habit to drink ample water throughout the day. By keeping your body well-hydrated, you can help prevent dryness and irritation, ultimately reducing the risk of developing boils.
Manage stress levels
Chronic stress can affect your well-being and weaken your immune system’s defenses. Discover stress-management techniques that work for you, such as regular exercise, practicing mindfulness or meditation, deep breathing exercises, or finding enjoyable activities that help you unwind. Prioritizing your mental well-being can positively impact your skin health and reduce the likelihood of developing boils.
Choose comfortable clothing
Opt for clothing made from breathable fabrics and avoid wearing overly tight or restrictive garments. These can create friction and trap sweat, providing an environment conducive to bacterial growth. By selecting loose-fitting, comfortable clothing, you allow proper airflow and minimize the chances of skin irritation and subsequent boil formation.
Practice proper wound care.
Promptly clean and care for any cuts, scrapes, or other skin injuries. Gently cleanse the affected area with mild soap and water, apply a suitable antiseptic ointment, and cover it with a sterile bandage until it fully heals. By practicing good wound care, you reduce the risk of bacterial entry and the development of boils.
Shave with care
If shaving is part of your grooming routine, take precautions to minimize the chances of ingrown hairs and subsequent boil formation. Use a clean, sharp razor and shave toward hair growth. Apply shaving cream or gel to lubricate the skin and reduce irritation. These measures help protect your skin from potential inflammation and the formation of painful boils.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Strive to maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Being overweight or obese can contribute to skin folds and increased sweat production, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of boils and support overall skin health.
Limit smoking and alcohol consumption.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken your immune system and impair its ability to fight off infections effectively. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can improve your immune system’s functioning, reducing the likelihood of developing boils.
Remember, consistency is key when implementing these lifestyle tips. While these strategies can be beneficial, it’s always prudent to seek personalized advice and guidance from a healthcare professional if you have concerns or experience persistent issues.
By making these positive lifestyle changes, you can proactively manage and prevent boils, promoting healthier skin and overall well-being.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
Dealing with boils can psychologically impact a person’s self-esteem, body image, and overall well-being. Coping with physical discomfort, pain, and potential scarring can be challenging. Here are some strategies to help manage the psychological impact of boils:
- Seek support:
-
- Reach out to friends, family, or support groups who can provide understanding and empathy. Sharing your experiences and feelings can alleviate the emotional burden.
- Educate yourself:
-
- Learn more about boils, their causes, and treatment options. Understanding the condition can empower you to care for yourself better and make informed decisions.
- Practice self-care:
-
- Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, exercise, or spending time in nature.
- Prioritize self-care practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness to reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
- Consult a mental health professional:
-
- If the psychological impact overwhelms your daily life significantly, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor who can provide guidance and support.
- Focus on positive aspects:
-
- While boils can be frustrating, remember that they are common and manageable conditions. Maintain a positive mindset and focus on your progress in managing and treating them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, boils are common skin infections that cause discomfort and frustration. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing and preventing them effectively. While medical interventions are often necessary, home remedies can provide additional relief and support healing. It’s important to remember that prevention plays a vital role, and adopting good hygiene practices, supporting a healthy immune system, and practicing self-care are essential. Lastly, consider the psychological impact of boils; seek support and guidance when needed. With the right information, care, and support, you can effectively navigate the journey of dealing with boils for a happier, healthier you.
FAQs
What are boils, and why do they occur?
Boils are painful, pus-filled bumps that develop on the skin. They occur when bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus, infect a hair follicle or oil gland. The infection leads to inflammation and the formation of a tender lump.
How can I treat a boil at home?
Home treatment for boils includes applying warm compresses to the affected area several times a day. This helps to promote drainage and relieve pain. It’s important to avoid squeezing or popping the boil, as it can worsen the infection. Keeping the area clean and practicing good hygiene is also crucial.
When should I seek medical attention for a boil?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if the boil is large, extremely painful, or accompanied by symptoms such as fever, red streaks, or spreading infection. Additionally, a healthcare professional should evaluate recurring boils in sensitive areas like the face, groin, or breast.
Are there any natural remedies for boils that I can try?
Yes, some natural remedies can help with boils. Tea tree oil, with its antimicrobial properties, can be applied topically to aid in killing bacteria. Aloe vera gel can soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. Turmeric paste and garlic juice are also known for their antibacterial properties and may assist in the healing process.
What are some effective preventive measures to avoid boils?
To reduce the risk of boils, practicing good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing and keeping the skin clean, is important. Avoid sharing personal items and maintain proper wound care for cuts or scrapes. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding tight-fitting clothing can also help prevent the occurrence of boils.
References
Mayo Clinic – Boils and Carbuncles
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making any decisions regarding your health. The author and publisher of this article are not liable for any potential consequences arising from using the information provided.