Cellulitis, a common yet often misunderstood skin infection, poses a significant threat to individuals of all ages. This article aims to shed light on this condition, providing a comprehensive overview of its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. By understanding the intricacies of cellulitis, we can empower ourselves to recognize the signs early on, seek prompt medical attention, and take proactive measures to prevent its recurrence.
What is Cellulitis?
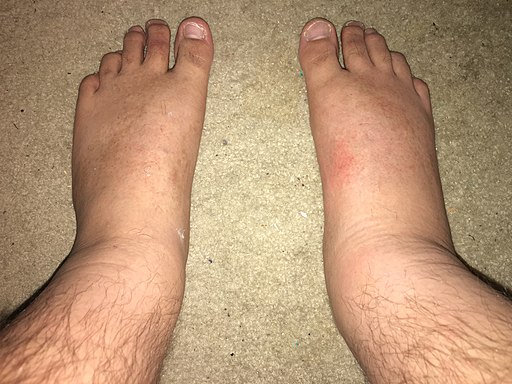
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection affecting the deeper skin layers and underlying tissues. Unlike superficial skin infections, cellulitis can spread rapidly and pose serious health risks if left untreated. The primary culprits behind cellulitis are the bacteria Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, which enter the skin through cuts, wounds, or breaks. Although cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, it commonly affects the legs and face.
Signs and Symptoms of Cellulitis
Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of cellulitis is crucial for timely intervention. The affected area typically displays redness, warmth, and tenderness, accompanied by swelling and inflammation. As the infection progresses, the skin may develop blisters, abscesses, or even a feeling of tightness. Individuals with cellulitis may also experience systemic symptoms such as fever and chills, indicating the spread of infection.
Understanding the Causes of Cellulitis
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria breach the skin’s protective barrier, gaining access to the underlying tissues. Common entry points include cuts, insect bites, surgical wounds, and skin conditions like eczema. In addition, individuals with compromised immune systems, such as diabetes or HIV, are at a higher risk of cellulitis. Therefore, maintaining healthy skin barriers through proper hygiene and wound care is essential for preventing this infection.
Complications and Dangers of Untreated Cellulitis

Failure to address cellulitis promptly can result in severe complications. The infection can spread to deeper tissues, forming abscesses and, in severe cases, sepsis. Long-term complications may include chronic swelling, tissue damage, and reduced quality of life. To mitigate these risks, seeking immediate medical attention upon suspecting cellulitis is crucial.
Diagnosing Cellulitis: What to Expect
Diagnosing cellulitis involves a thorough medical history evaluation and physical examination. The healthcare professional will assess the affected area, looking for signs of infection and ruling out other conditions. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI and laboratory tests such as blood cultures may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Effective Treatment Options for Cellulitis
Cellulitis treatment revolves around antibiotic therapy, eradicating the underlying bacterial infection. Depending on the severity of the infection, oral or intravenous antibiotics may be prescribed. It is crucial to complete the course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve. Additional measures like the elevation of the affected limb, pain management, and proper wound care can aid in symptom relief and expedite recovery.
Preventing Cellulitis: Proactive Measures for Healthy Skin
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of cellulitis. Adopting proactive measures and incorporating healthy habits into our daily routine can minimize the likelihood of developing this skin infection. Here are some essential practices to help maintain healthy skin and prevent cellulitis:
Practicing Good Hygiene
Regular handwashing with soap and water is crucial in preventing the spread of bacteria that can cause cellulitis. Make it a habit to wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling any cuts, wounds, or areas of compromised skin. In addition, keep your body clean by bathing or showering regularly, paying attention to areas prone to moisture buildup or sweat.
Proper Wound Care
Any break in the skin, including cuts, scrapes, or insect bites, can serve as an entry point for bacteria. Promptly clean and disinfect any wounds using mild soap and water. Cover them with clean bandages to protect them from contamination. Remember to change the bandages regularly, especially if wet or dirty.
Moisturizing the Skin
Dry and cracked skin is more susceptible to bacterial invasion. To maintain a healthy skin barrier, use a gentle moisturizer regularly. Look for products that are fragrance-free and hypoallergenic to avoid potential irritants. Focus on moisturizing areas prone to dryness, such as the legs, arms, and hands.
Avoiding Excessive Moisture
Excessive moisture on the skin, especially in warm and humid environments, can create an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. Keep your skin dry, especially in areas prone to sweat, such as the armpits and groin. Use absorbent powders or antiperspirants to minimize moisture buildup.
Protecting the Skin
Preventing skin injuries is an essential aspect of cellulitis prevention. Wear protective gear, such as gloves, when working with sharp objects or engaging in activities that may pose a risk of cuts or punctures. In addition, use insect repellents to avoid insect bites, as they can also introduce bacteria into the skin.
Maintaining a Healthy Immune System
A strong immune system is crucial in fighting off infections, including cellulitis. Maintain a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support your immune system. In addition, get regular exercise, manage stress levels, and prioritize adequate sleep to ensure optimal immune function.
Education and Awareness
Spread the knowledge about cellulitis and its prevention among your family, friends, and community. By raising awareness, you can help others recognize the importance of proper wound care, hygiene practices, and overall skin health. In addition, encourage regular check-ups and prompt medical attention for any signs of infection.
Recurrent Cellulitis: Causes and Prevention Strategies
While cellulitis is often a one-time occurrence, some individuals may experience recurrent episodes. Recurrent cellulitis can significantly impact the quality of life and require proactive measures to prevent future episodes. Understanding the underlying causes and adopting prevention strategies are key. Here’s what you need to know:
Identifying Underlying Causes
Recurrent cellulitis may be associated with certain risk factors and underlying conditions. For example, chronic edema (swelling) or lymphatic dysfunction can impair the body’s ability to fight infection. In addition, skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, which weaken the skin barrier, can also contribute to recurrent cellulitis. Identifying these factors can help tailor preventive measures accordingly.
Addressing Risk Factors
Once the underlying causes are identified, addressing and managing these risk factors becomes essential in preventing recurrent cellulitis. For example, if chronic edema contributes to recurrent episodes, compression therapy, exercise, and elevation of the affected limb can help reduce swelling and improve circulation. In addition, treating underlying skin conditions with appropriate medications and therapies can also strengthen the skin barrier.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent cellulitis. For example, if obesity is a contributing factor, adopting a healthy diet and exercising regularly to achieve and maintain a healthy weight can be beneficial. In addition, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption supports overall skin health and immune function.
Long-Term Management
Individuals with recurrent cellulitis may benefit from long-term management plans developed with healthcare professionals. Regular follow-ups can help monitor the condition and address any new risk factors that may arise. In addition, implementing preventive measures consistently, such as moisturizing the skin, practicing good hygiene, and promptly treating any skin injuries or infections, is crucial for reducing the likelihood of future cellulitis episodes.
Support and Education
Living with recurrent cellulitis can be physically and emotionally challenging. Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or online communities to connect with others who share similar experiences. In addition, education about the condition and preventive strategies can empower individuals to take control of their health and reduce the impact of recurrent cellulitis.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Doctor
Regarding cellulitis, seeking timely medical attention is paramount for effective treatment and prevention of complications. While self-care measures can be effective in mild cases, certain situations warrant consulting a healthcare professional. Here are some indications to seek medical help:
Worsening Symptoms
If the symptoms of cellulitis worsen despite self-care measures, it is essential to consult a doctor. Increased redness, swelling, warmth, or tenderness around the affected area may indicate progression of the infection. Seeking medical attention can prevent the spread of the infection to deeper tissues and reduce the risk of complications.
Systemic Symptoms
The presence of systemic symptoms suggests a more severe infection. If you experience fever, chills, persistent fatigue, or general malaise, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. These symptoms may indicate the infection is spreading beyond the localized area and require more aggressive treatment.
Lack of Improvement
If there is no improvement in symptoms after a few days of self-care measures, seeking medical attention is advisable. A delayed response to self-care may indicate a need for antibiotic treatment or a more accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional can evaluate the condition, prescribe appropriate antibiotics, and provide guidance on further management.
Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, HIV, or compromised immune systems, are at a higher risk of developing complications from cellulitis. Therefore, if you have any underlying health conditions, it is important to consult a doctor promptly when cellulitis is suspected to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent further complications.
Severe Symptoms
In some cases, cellulitis can lead to severe symptoms and complications that require immediate medical attention. For example, if you experience rapidly spreading redness, severe pain, the formation of large abscesses, or difficulty moving the affected limb, seek emergency medical care without delay.
Remember, trusting your instincts and seeking professional help can prevent the worsening of cellulitis and reduce the risk of serious complications. A healthcare professional will evaluate your symptoms, diagnose accurately, and guide you through the most appropriate treatment options.
The Role of Antibiotics in Cellulitis Treatment
Effective cellulitis treatment often involves using antibiotics to eliminate the underlying bacterial infection. Antibiotics work by targeting and killing the bacteria responsible for the infection. Here are key points to understand about antibiotics for cellulitis treatment:
Antibiotic Selection
The choice of antibiotics depends on various factors, including the severity of the infection, the suspected bacteria, and any underlying health conditions. Oral antibiotics such as penicillin, cephalosporins, or erythromycin may be prescribed in mild cases. For more severe infections or cases that do not respond to oral antibiotics, intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be necessary in a hospital setting.
Full Course Completion
It is crucial to complete the course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the course is finished. Prematurely stopping antibiotics can allow the bacteria to survive and potentially develop antibiotic resistance. Therefore, compliance with the prescribed dosage and duration is essential for effective treatment and to prevent the recurrence of cellulitis.
Symptom Relief
Alongside antibiotics, certain measures can help relieve symptoms and promote healing. Elevating the affected limb, applying warm compresses, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation if a healthcare professional recommends it. It is important to follow healthcare providers’ guidance on pain management for cellulitis.
Follow-up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are essential during and after cellulitis treatment. These appointments allow the healthcare provider to monitor your progress, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and make any necessary adjustments to the antibiotic regimen. Follow-up visits also allow you to address any concerns or questions.
Potential Side Effects
Like any medication, antibiotics can have side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, inform your healthcare provider promptly. They can assess the situation and make necessary changes to your treatment plan.
Antibiotic Resistance
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a growing concern. To minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to take antibiotics as prescribed, avoid unnecessary antibiotic use, and complete the full course of treatment. Additionally, practicing preventive measures, such as proper wound care and infection control, can help reduce the need for antibiotics and limit the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Surgical Intervention for Cellulitis: When Is It Necessary?
Usually, cellulitis can be effectively treated with antibiotics and self-care measures. However, there are situations where surgical intervention may be necessary to address complications or facilitate healing. Here are some instances when surgical intervention may be required:
Abscess Drainage
If localized pus (abscess) collection forms within the affected area, your healthcare provider may recommend drainage. This procedure involves making a small incision to release the pus and relieve pressure. Abscess drainage helps promote healing and reduces the risk of the infection spreading.
Surgical Debridement
Surgical debridement may be necessary in severe cases of cellulitis with extensive tissue damage or necrotic (dead) tissue. During this procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged or dead tissue, allowing healthy tissue to regenerate and aiding in healing.
Lymphatic Surgery
Surgical intervention to improve lymphatic drainage may be considered for individuals with recurrent cellulitis associated with lymphatic dysfunction. Various surgical techniques, such as lymphovenous anastomosis or lymphatic-venous shunt procedures, can help restore lymphatic flow and reduce the risk of future episodes.
Skin Grafting
Skin grafting may be performed in cases of significant skin loss or non-healing wounds. This procedure involves transplanting healthy skin from one area of the body (donor site) to the affected area (recipient site) to promote wound healing and restore the skin barrier.
It’s important to note that surgical intervention is typically reserved for specific situations and is determined by the healthcare provider based on individual patient needs. They will assess the cellulitis’s severity, complications, and potential benefits of surgical intervention.
Psychological Impact of Cellulitis: Coping Strategies and Emotional Well-being
Cellulitis not only affects physical well-being but can also have psychological and emotional implications. Therefore, coping with the challenges associated with cellulitis is essential for overall well-being. Here are some strategies to promote emotional resilience and psychological well-being:
Seek Support
Contact friends, family, or support groups who can provide emotional support and understanding. Sharing your experiences and concerns with others facing similar challenges can be comforting and help alleviate feelings of isolation.
Educate Yourself
Learn more about cellulitis to understand the condition and treatment options. Knowledge can empower you to actively participate in your care, ask relevant questions, and make informed decisions about your treatment.
Practice Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate cellulitis’s physical symptoms and emotional impact. Engage in stress-reducing activities that work for you, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy and relaxation.
Maintain a Positive Outlook
It’s normal to experience frustration, anxiety, or sadness due to cellulitis. However, focusing on the positive aspects of your life and practicing gratitude can help maintain a positive outlook. Celebrate small victories, practice self-compassion, and remind yourself that healing takes time.
Engage in Self-Care
Prioritize self-care activities that promote overall well-being. For example, engage in activities that bring you pleasure and relaxation, such as reading, listening to music, taking walks in nature, or practicing mindfulness. Taking care of your emotional and mental health is as important as physical care.
Seek Professional Help
If distress or anxiety persists, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor. They can provide guidance, coping strategies, and support tailored to your needs.
Remember, managing the psychological impact of cellulitis is an integral part of your overall recovery. Prioritize self-care, seek support, and practice resilience to navigate the emotional challenges that may arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellulitis is a common and potentially serious skin infection that requires prompt attention and proper treatment. By understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin health and minimize the risk of infection.
Prompt medical attention, adherence to prescribed treatments, and practicing preventive measures are crucial. Additionally, recognizing the signs of complications and seeking timely intervention is essential.
Taking care of one’s mental well-being and seeking support are also important aspects of recovery. By staying informed and proactive, we can effectively manage cellulitis and reduce its impact on our lives. Consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment if you suspect cellulitis or have concerns.
FAQs
Can cellulitis be contagious?
Cellulitis itself is not contagious. Instead, it is caused by bacteria that normally reside on the skin or the environment. However, if the bacteria enter a break in the skin and cause an infection, it is important to practice good hygiene and take precautions to prevent the spread of the infection to others.
Can cellulitis be prevented?
While preventing cellulitis is not always possible, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing an infection. These include practicing good hygiene, keeping the skin clean and moisturized, promptly treating any cuts or wounds, avoiding prolonged exposure to dirty or contaminated environments, and managing underlying conditions that can increase the risk of cellulitides, such as edema or diabetes.
How long does it take for cellulitis to heal?
The healing time for cellulitis can vary depending on factors such as the severity of the infection, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of treatment. Mild cases of cellulitis may resolve within a week or two with appropriate treatment. However, more severe cases or those with complications may take longer to heal. Therefore, following the prescribed treatment plan and seeking medical advice if the symptoms worsen or do not improve is important.
Can cellulitis recur?
Yes, cellulitis can recur, especially in individuals with underlying risk factors such as chronic edema, skin conditions, or compromised immune systems. Therefore, it is important to work closely with healthcare providers to identify and address the underlying causes of recurrent cellulitis and take preventive measures to minimize the risk of recurrence.
Can cellulitis be treated at home?
In most cases, cellulitis requires medical treatment, including antibiotics. Mild cases of cellulitis may be managed with oral antibiotics at home under the guidance of a healthcare professional. However, seeking medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan is important. Severe cases or those with complications may require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics or surgical intervention.
Can I speed up the healing process of cellulitis?
While there is no guaranteed way to speed up the healing process, certain measures can support the healing and recovery from cellulitis. These include following the prescribed treatment plan, taking antibiotics as directed, practicing proper wound care, keeping the affected area elevated, applying warm compresses, and taking measures to support overall health, such as eating a nutritious diet, staying hydrated, and getting adequate rest.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Cellulitis: All you need to know
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Cellulitis can vary in severity, and individual cases may require different treatments. Always consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan based on your condition. The author and publisher disclaim any liability for any adverse effects resulting from the use or application of the information presented in this article.