Granuloma Annulare (GA) often remains mysterious, even though many encounter its impacts. This skin condition, characterized by distinct rashes and bumps, weaves a complex story that intertwines medical science, lifestyle, and emotional well-being. The journey to understanding Granuloma Annulare is not just about identifying red, ring-like lesions on the skin; it’s about unraveling the intricacies behind its occurrence, the challenges in its diagnosis, and the various strategies for managing its symptoms.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dive deep into the world of Granuloma Annulare. From its basic definition to the latest research, we aim to cover every aspect of this condition. Whether you’re recently diagnosed, a caregiver, or just curious about GA, this article promises to be your one-stop resource. Expect to discover detailed insights into the types of GA, common symptoms, potential causes, and the latest treatment options.
But we won’t stop there. Understanding GA goes beyond medical facts. It’s about grasping its impact on daily life and mental health. So, we’ll also explore the psychological aspects and share valuable advice on lifestyle modifications and home remedies that can make a difference.
By the end of this read, you’ll gain a thorough understanding of Granuloma Annulare and gather practical tips and knowledge to navigate this condition confidently. So, let’s embark on this informative journey together, unraveling the layers of GA, one fact at a time.
What is Granuloma Annulare?

Granuloma Annulare: This term might sound complex, but it describes a skin condition that’s more common than you might think
. Granuloma Annulare, often abbreviated as GA, is a benign (non-cancerous) skin disorder. It manifests as raised, sometimes ring-shaped rashes or lumps under the skin. These distinctive marks are GA’s calling card, making it recognizable to those familiar with it.
Who Gets Granuloma Annulare?
Primarily, GA makes its presence known to children and young adults. Still, it doesn’t discriminate by age – anyone can experience it. Interestingly, women are twice as likely to be affected as men. This higher prevalence in women adds a unique dimension to the condition’s understanding.
The Types of Granuloma Annulare
Granuloma Annulare isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition. It comes in several types, each with its characteristics:
- Localized Granuloma Annulare: The most common form, where circular rashes appear in one area.
- Generalized Granuloma Annulare: Here, the bumps spread over a larger skin area.
- Subcutaneous Granuloma Annulare: This type goes deeper, forming lumps under the skin.
- Perforating Granuloma Annulare: Identified by painful bumps, often on hands and fingers.
- Patch Granuloma Annulare: It features flat rash areas in patches on the skin.
Each type of GA tells a different story through the skin’s appearance, and understanding these types helps tailor the approach to management and treatment.
Symptoms and Identification of Granuloma Annulare

Regarding Granuloma Annulare (GA), the symptoms are as unique as the condition itself. Understanding these symptoms is key to early identification and management. Here, we’ll explore what to look for and how GA makes itself known.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The most telltale sign of GA is its distinctive rash. These aren’t your everyday rashes. They have a certain flair, often forming circular or ring-like patterns. Let’s break down what these symptoms typically look like:
- Raised Bumps: The rash usually appears as small, firm bumps (papules) that may merge into larger areas.
- Color: These bumps are often reddish or skin-colored but can also have a purple hue, especially in darker skin tones.
- Texture: The affected area might feel smooth and firm to the touch.
- Common Areas: GA frequently appears on the hands, feet, elbows, and knees. However, it can show up on any part of the body.
Types and Their Symptoms
Different types of GA present different symptoms. For instance:
- Localized GA often sticks to one area, like the ankles or wrists, and doesn’t spread much.
- Generalized GA, on the other hand, can cover large areas like the arms or legs.
- In Subcutaneous GA, you might feel lumps under the skin, especially in children.
- Perforating GA can sometimes be itchy or painful, slightly different from usually painless types.
- Patch GA presents larger, flatter areas of rash and is less common than the other types.
Beyond the Rash
While rashes are the main event with GA, there’s more to the story:
- Symptom Duration: GA can be a fleeting visitor or a long-term resident. Some cases clear up within a few months, while others can linger for years.
- Reoccurrence: GA can be quite the encore performer, often reappearing in the same spot even after treatment.
- Physical Discomfort: Generally, GA isn’t painful or itchy, but don’t be surprised if it occasionally breaks this rule, especially in the perforating type.
Causes and Risk Factors of Granuloma Annulare
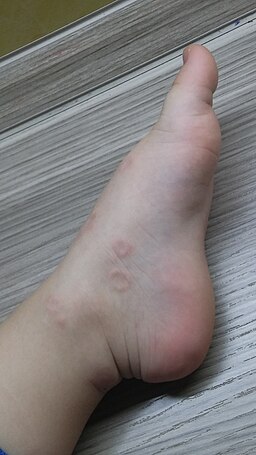
Delving into the causes and risk factors of Granuloma Annulare (GA) is like navigating a maze with many turns but no clear path. While the exact cause of GA remains a puzzle, researchers have identified several factors that might play a role. Here, we’ll explore what might trigger this unique skin condition and who is most at risk.
The Elusive Cause
One of the most intriguing aspects of GA is its mysterious origin. Despite extensive research, the precise cause continues to elude medical experts. However, several theories and observations shed light on possible triggers:
- Immune System Response: GA might result from an overactive immune response. Your immune system, usually the body’s defender against harm, might mistakenly target your skin cells, leading to the characteristic rashes of GA.
- Genetic Factors: There’s some evidence suggesting a genetic predisposition to GA. If your family tree has branches with GA, you might also be more likely to develop it.
Environmental and Health Triggers
The environment around us and our health conditions can influence the likelihood of developing GA:
- Skin Injuries: In some cases, skin injuries like insect bites or sunburns can trigger GA. It’s as if these injuries set off a chain reaction, ending in those distinctive rashes.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as allopurinol (used for gout), have been linked to GA. These medications might kickstart an immune response that manifests as GA.
- Existing Health Conditions: People with some health conditions seem more prone to GA. Notably, those with diabetes, especially Type 1, and thyroid disorders, are at a higher risk.
Who is at Risk?
Understanding who is most likely to develop GA can help in early identification and management:
- Age and Gender: GA can appear at any age but is most common in children and young adults. Women are more frequently affected than men, suggesting hormonal factors might also play a role.
- Family History: A family history of GA increases your chances of developing it, pointing towards a genetic component.
Diagnosis of Granuloma Annulare
When it comes to diagnosing Granuloma Annulare (GA), the approach is as meticulous as it is insightful. Although GA has distinctive symptoms, confirming the diagnosis often requires a closer look. This section will guide you through the steps and tests involved in diagnosing GA.
The First Step: Physical Examination
The journey to a GA diagnosis typically starts with a physical examination. If you or your doctor notice unusual rashes or lumps on your skin, GA could be a suspect. During the examination, your healthcare provider will consider:
- The appearance of the Rash: GA rashes have a characteristic look – raised, sometimes ring-shaped, and often reddish or skin-colored.
- Location and Spread: The areas where the rash appears and how it has spread across the skin are crucial clues.
Going Deeper: Skin Biopsy
A physical examination alone isn’t always enough. To confirm GA, a skin biopsy is often the next step. Here’s what it involves:
- Procedure: A small piece of skin from the affected area is gently removed.
- Analysis: This sample is then examined under a microscope in a lab. The goal is to look for specific patterns and cells typical of GA.
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Conditions
GA can be a master of disguise, often resembling other skin conditions. Part of diagnosing GA involves ruling out these look-alikes. Conditions that might be mistaken for GA include:
- Ringworm: A fungal infection with a similar ring-like rash.
- Eczema: Known for causing itchy, inflamed skin.
- Psoriasis: Characterized by scaly, red patches.
Treatment Options for Granuloma Annulare
Navigating the treatment landscape for Granuloma Annulare (GA) requires a tailored approach, balancing effectiveness with individual needs. While there’s no one-size-fits-all remedy, several treatment options offer relief and improve skin appearance. This section outlines the various treatments available, providing a comprehensive view of how GA can be managed.
Overview of Treatment Approach
The overarching goal in treating GA is to alleviate any discomfort and expedite the fading of skin lesions. It’s important to remember that GA often resolves independently without intervention. However, when treatment is necessary, several factors guide the choice of therapy:
- Severity and Spread: The extent of skin involvement often dictates treatment intensity. Localized forms may require less aggressive approaches than generalized GA.
- Symptom Management: For some, the primary concern might be itching or cosmetic appearance, which can influence the treatment choice.
- Patient Preferences and Health: Individual preferences and overall health also play a crucial role in deciding the treatment pathway.
In the treatment of GA, patience is key. Responses to treatment can vary, and it might take time to see improvement. Also, it’s common for GA to reappear after treatment, so long-term management strategies are often necessary.
Next, we will delve into specific medications and therapies used to treat GA, highlighting their applications and effectiveness. Stay tuned as we explore each treatment option in detail, offering insights into how they can relieve and improve the quality of life for those dealing with Granuloma Annulare.
Medications for Granuloma Annulare
When it comes to treating Granuloma Annulare (GA), medications play a pivotal role. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and speed up the disappearance of skin lesions. Here’s an overview of the main types of medications used in the management of GA:
Topical Corticosteroids:
Often the first line of treatment, these creams and ointments are applied directly to the rash. They reduce inflammation and can be particularly effective for mild or localized GA. The strength of the corticosteroid and the duration of use depend on the severity of the symptoms.
Corticosteroid Injections:
For more stubborn or severe lesions, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected area can be more effective. These injections can help flatten the lesions and reduce redness, especially in cases where topical treatments haven’t worked.
Oral Medications:
In cases of widespread GA, oral medications may be necessary. These can include:
Antimalarials:
Drugs like hydroxychloroquine are sometimes used, especially in generalized GA. They are thought to work by modulating the immune response.
Isotretinoin:
Commonly known for treating severe acne, isotretinoin has also shown effectiveness in some GA cases. It’s particularly useful when the condition is resistant to other treatments.
Other Immune Modulators:
Medications that alter the immune response, like dapsone or methotrexate, can be used in more severe or resistant cases of GA.
Biologics and Newer Therapies:
Recently, drugs that target specific parts of the immune system, known as biologics, have been explored for GA. While not a standard treatment, they offer promise for cases that don’t respond to conventional therapies.
It’s important to note that medication effectiveness can vary from person to person, and some of these treatments can have side effects. Close consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to find the most suitable and safe treatment plan.
By combining medical guidance with an understanding of these medication options, individuals with GA can navigate their treatment journey with greater confidence. Next, we’ll explore additional therapeutic approaches that complement medications in treating Granuloma Annulare.
Light Therapy and Cryotherapy in Granuloma Annulare Treatment
Aside from medications, other therapeutic approaches like light therapy and cryotherapy offer alternative routes in treating Granuloma Annulare (GA). These methods can be particularly beneficial when medications alone are insufficient or unsuitable. Let’s explore how these treatments work and their role in managing GA.
Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
Light therapy, or phototherapy, involves exposing the skin to specific types of light under controlled conditions. This method can be especially effective for widespread GA lesions. Here’s how it works:
Types of Light Therapy:
- Ultraviolet B (UVB) Therapy: This involves exposure to UVB light, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Psoralen Plus Ultraviolet A (PUVA): Combines a drug called psoralen with UVA light. Psoralen makes the skin more exposed to light, enhancing the effectiveness of UVA therapy.
- Procedure: Sessions usually occur in a dermatologist’s office, and the frequency depends on the severity of GA.
- Benefits: Light therapy can be an effective alternative for those who can’t use or haven’t responded to topical or systemic medications.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves the application of intense cold to freeze and remove abnormal tissue. For GA, it can be a viable option for localized lesions. Here’s a closer look:
- Procedure: A dermatologist applies liquid nitrogen to the GA lesions, freezing the abnormal skin cells.
- Effectiveness: Cryotherapy can be particularly effective for small, localized GA patches. It can help reduce the size and appearance of the lesions.
- Considerations: While generally safe, cryotherapy can cause temporary side effects like redness, blistering, or scarring. Due to these potential side effects, it’s not typically used for widespread GA.
Both light therapy and cryotherapy offer unique benefits and can be tailored to individual needs. They provide additional options in the multifaceted approach to GA treatment, especially for cases that are difficult to manage with medications alone.
By understanding these therapies, individuals dealing with GA can make knowledgeable decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers. Next, we will explore other supportive treatments and lifestyle modifications that complement medical interventions in managing Granuloma Annulare.
Emerging Treatments for Granuloma Annulare: The Role of Tofacitinib
In the evolving landscape of Granuloma Annulare (GA) treatment, emerging therapies like Tofacitinib offer new hope, especially for those with severe or treatment-resistant forms of the condition. Let’s explore this novel treatment and its potential in managing GA.
Tofacitinib: A New Horizon in GA Treatment
Tofacitinib is an oral medication originally approved for rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. It belongs to a class of drugs known as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which modulate the immune system. Here’s how it’s making a difference in GA treatment:
- Mechanism of Action: Tofacitinib targets specific pathways in the immune system that contribute to inflammation. Inhibiting these pathways can reduce the inflammatory processes that lead to GA lesions.
- Research and Studies: Recent studies have shown promising results. For instance, a study involving patients with severe GA showed significant improvement with Tofacitinib. In some cases, patients experienced complete clearance of skin lesions.
- Administration: Tofacitinib is administered orally, making it a convenient option for systemic treatment.
Considerations and Future Potential
While Tofacitinib and similar JAK inhibitors represent a significant advancement in GA treatment, there are important considerations:
- Side Effects: As with any medication, there are potential side effects. These can include increased risk of infections, changes in blood counts, and others.
- Approval and Accessibility: Currently, Tofacitinib is not specifically approved for GA, meaning its use for this condition is off-label. However, ongoing research may change this in the future.
- Patient Selection: Due to its potent immune-modulating effects, Tofacitinib may be reserved for severe or refractory cases of GA.
Emerging treatments like Tofacitinib are changing the game in GA management, offering effective options for those who have struggled to find relief with traditional therapies.
As research progresses, these treatments are expected to become integral to the GA treatment arsenal.
The exploration of Tofacitinib underscores the dynamic nature of GA treatment and the importance of ongoing research in uncovering new therapeutic avenues. Next, we will delve into lifestyle modifications and supportive therapies that can enhance the overall management of Granuloma Annulare, emphasizing the holistic care of individuals affected by this condition.
Effectiveness and Potential Side Effects of Granuloma Annulare Treatments
When managing Granuloma Annulare (GA), understanding treatments’ effectiveness and potential side effects is crucial. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions and manage expectations. Here, we delve into how effective various GA treatments are and what side effects one might encounter.
Effectiveness of Treatments
The effectiveness of GA treatments can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of GA, its severity, and individual patient responses. Let’s break it down by treatment type:
- Topical and Injected Corticosteroids: Often effective for localized GA, they can reduce the appearance of lesions. However, some cases may not respond as well, especially in generalized GA.
- Oral Medications: These can be effective for more severe or widespread GA, but results can take time. Not all patients see complete clearance.
- Light Therapy and Cryotherapy: Generally effective for certain types of GA, especially when combined with other treatments. However, their effectiveness can vary.
- Emerging Treatments (like Tofacitinib): Show promise in severe or treatment-resistant cases, with some patients experiencing significant improvement.
Potential Side Effects
While treatments can be effective, they may come with side effects. Awareness of these is important for managing treatment:
- Corticosteroids: Topical steroids can cause skin thinning, stretch marks, and local skin changes, especially with prolonged use. Injected steroids may cause temporary pain or skin discoloration at the injection site.
- Oral Medications: These can have a range of side effects, from gastrointestinal issues to effects on liver function, depending on the medication.
- Light Therapy: Can cause skin aging, increased risk of skin cancer, and burns if not properly administered.
- Cryotherapy: This may lead to blistering, scarring, or changes in skin pigmentation.
- Tofacitinib and Similar Drugs: Potential risks include increased susceptibility to infections, changes in blood counts, and others.
It’s important for patients and healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment option. Monitoring and regular follow-ups can help manage any side effects that arise.
In summary, while there is no one-size-fits-all solution for GA, a range of effective treatments is available. Understanding their potential side effects helps in making informed choices about management strategies.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Granuloma Annulare
Managing Granuloma Annulare (GA) extends beyond medical treatments. Integrating certain lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can significantly manage symptoms and improve overall skin health. This section explores practical and natural ways to support the treatment of GA and enhance well-being.
Skin Care Routine
Proper skin care is fundamental in managing GA. Here are some tips:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized can prevent dryness and reduce irritation. Look for products that are fragrance-free and appropriate for sensitive skin.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild soaps or cleansers that don’t strip the skin’s natural oils.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid skin products with harsh chemicals or irritants, which can exacerbate GA symptoms.
Sun Protection
Sun exposure can sometimes trigger GA flare-ups. Protecting your skin from the sun is therefore crucial:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to all exposed skin, especially if your GA lesions are in sun-exposed areas.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Hats, long sleeves, and other protective clothing can provide an additional barrier against UV rays.
Healthy Diet
Diet can influence skin health. While there’s no specific “GA diet,” some general guidelines can be helpful:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential nutrients that can support skin health.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake is important for maintaining skin hydration.
- Limit Certain Fats: Some studies suggest that reducing the intake of certain fats (like cholesterol and triglycerides) might benefit GA.
Stress Management
Stress can impact GA, so managing stress levels is important:
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a great stress reliever and can improve overall health.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough rest, as sleep deprivation can exacerbate stress.
Avoiding Triggers
If you notice certain activities or substances trigger your GA, try to avoid them. This could include specific skincare products, environments, or even certain foods.
Community and Support
Connecting with others who have GA can provide emotional support and practical advice. Look for online forums, support groups, or local communities.
Individuals with GA can proactively contribute to their skin health and overall well-being by incorporating these lifestyle adjustments and home remedies. These measures, alongside medical treatments, can make a tangible difference in managing Granuloma Annulare.
Psychological Impact and Support for Granuloma Annulare
Living with Granuloma Annulare (GA) is not just a physical challenge; it can also have significant psychological implications. Recognizing and addressing these emotional aspects is crucial for holistic care. This section explores the psychological impact of GA and the importance of seeking and offering support.
Understanding the Emotional Toll
GA, especially when widespread or visible, can affect an individual’s self-esteem and body image. Here’s how:
- Self-Consciousness: Visible skin lesions can lead to feelings of self-consciousness or embarrassment, impacting social interactions and daily activities.
- Anxiety and Stress: Worrying about the appearance of the skin or the progression of GA can contribute to anxiety and stress.
- Depression: In some cases, the chronic nature of the condition and its visibility can lead to depression.
Seeking Emotional Support
Managing the psychological impact of GA is as important as treating the physical symptoms. Here are some ways to find support:
- Professional Counseling: Speaking with a mental health professional can provide strategies to cope with the emotional challenges of living with GA.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have GA can offer a sense of community and understanding. Whether online or in-person, support groups can provide a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
- Family and Friends: Discussing your feelings with loved ones can help them understand your experiences and offer support.
Coping Strategies
Developing personal coping strategies can also help manage the emotional impact of GA:
- Educate Yourself: Understanding your condition can empower you and reduce anxiety about the unknown.
- Focus on What You Can Control: Concentrating on treatment and lifestyle changes can provide a sense of control over your condition.
- Practice Self-Care: Engaging in activities you enjoy and that relax you can improve your mental well-being.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can increase mood and reduce stress.
Building Resilience
Building emotional resilience is key in living with GA. This involves:
- Acceptance: Acknowledging the condition and its impact on your life is the first step in moving forward.
- Positive Mindset: Focusing on the positives, however small, can shift your perspective and improve overall well-being.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Setting achievable goals in terms of treatment and daily life can provide a sense of accomplishment.
The psychological aspect of GA is a critical part of the overall condition management. It’s important to remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Recent Research and Future Directions in Granuloma Annulare
The landscape of Granuloma Annulare (GA) is continually evolving, with ongoing research shedding new light on this condition. Keeping abreast of the latest studies not only offers hope for more effective treatments but also deepens our understanding of GA. This section highlights recent breakthroughs and looks at what the future might hold in GA research and treatment.
Summary of Recent Studies
One of the most notable recent advancements in GA research comes from a study conducted by the Yale School of Medicine, focusing on the drug tofacitinib.
Yale Study on Tofacitinib:
- Background: Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, traditionally used in treating rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Its potential in treating GA was explored due to its immune-modulating properties.
- Study Findings: The study involved patients with severe, treatment-resistant GA. Remarkably, treatment with Tofacitinib resulted in significant improvement in these patients. In some cases, there was complete clearance of the skin lesions.
- Implications: These findings are particularly promising for individuals with severe GA who have not responded to traditional treatments. It opens a new avenue for therapy, highlighting the potential of JAK inhibitors in managing GA.
Other Notable Research:
- Exploring Genetic Factors: Ongoing studies are delving into the genetic aspects of GA, aiming to uncover genetic markers that could predict susceptibility or response to treatment.
- Understanding Immune Pathways: Research continues to explore the specific immune pathways involved in GA, which could lead to targeted therapies.
- Clinical Trials for New Therapies: Various clinical trials are underway to test new medications and combinations of treatments to find more effective ways to manage GA.
The recent research into GA, particularly studies like the Yale tofacitinib study, marks a significant step forward. These developments not only offer new hope for those affected by the condition but also pave the way for more targeted and useful treatments in the future.
Ongoing Clinical Trials in Granuloma Annulare
The pursuit of better treatments and a deeper understanding of Granuloma Annulare (GA) is an ongoing endeavor, with several clinical trials underway. These trials are crucial for validating new treatments, understanding the effectiveness of existing ones, and exploring the underlying mechanisms of GA. Let’s delve into the current landscape of these clinical trials and their potential impact on GA management.
New Medications and Therapies:
- Investigating New Drugs: Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of new pharmacological agents in treating GA. These include drugs with different mechanisms of action, such as newer immunomodulators and biological agents.
- Combination Therapies: Some trials are focused on understanding how combining existing treatments can provide better outcomes. For example, combining light therapy with topical treatments to enhance effectiveness.
Targeted Treatment Approaches:
- Personalized Medicine: Trials are increasingly looking at personalized approaches to treatment, considering individual variations in response to therapy. This involves tailoring treatments based on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Understanding Specific GA Types: Separate trials for different GA types (like generalized or localized) are important to understand the unique responses and best treatment protocols for each.
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety:
- Longitudinal Studies: Trials also focus on the long-term effects of GA treatments in terms of efficacy and safety. These studies are crucial for understanding different therapies’ potential long-term benefits and risks.
Quality of Life and Psychological Aspects:
- Assessing Impact on Well-Being: Some trials include components that assess the impact of treatments on patients’ quality of life, mental health, and overall well-being. This holistic approach is crucial in understanding the full impact of GA and its treatments.
These ongoing clinical trials represent the frontier of GA research, offering hope for more effective, personalized, and comprehensive treatment strategies. As these trials progress, they promise to bring new insights and advancements that could significantly improve the lives of those affected by Granuloma Annulare.
Future Potential Treatments and Research Areas in Granuloma Annulare
As we look toward the future in the realm of Granuloma Annulare (GA) research and treatment, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and innovations is vast. Building on current studies and clinical trials, the future of GA treatment is poised to become more effective, personalized, and holistic. Let’s explore the promising areas of research and potential treatments that are on the horizon for GA.
Advanced Biologic Therapies:
- Next-Generation Immunomodulators: The success of drugs like Tofacitinib opens the door for developing new biological agents that target specific immune pathways involved in GA.
- Customized Biologic Treatments: With advancements in genetic and molecular research, future therapies could be tailored to individual genetic profiles, increasing their effectiveness and reducing side effects.
Gene Therapy and Genetic Research:
- Gene Editing: Emerging techniques like CRISPR gene editing offer the potential to understand and possibly treat GA at the genetic level.
- Genetic Markers of GA: Identifying genetic factors contributing to GA could lead to predictive models and early intervention strategies.
Nanomedicine and Targeted Drug Delivery:
- Nanoparticle-Based Therapies: Using nanoparticles in drug delivery could enhance the precision and effectiveness of topical treatments, reducing systemic side effects.
- Localized Treatment Approaches: Future research may develop methods to target affected skin areas directly, improving treatment efficacy and minimizing impact on healthy skin.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors:
- Holistic Approaches: Research into the impact of diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors on GA could lead to more comprehensive management strategies.
- Preventative Measures: Understanding how these factors contribute to GA could lead to preventative guidelines and early intervention protocols.
Technological Integration in Treatment:
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Advancements in technology could facilitate remote management of GA, making treatments more accessible and efficient.
- AI and Machine Learning: Using artificial intelligence to diagnose and predict treatment responses could revolutionize GA management.
The future of GA research and treatment is rich with possibilities, from genetic insights to advanced therapeutics and integrated technological solutions. As we unravel this condition’s complexities, the hope for more effective, personalized, and patient-centric treatments grows stronger.
With these advancements on the horizon, the overall outlook for individuals with Granuloma Annulare is increasingly optimistic.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path of Granuloma Annulare
As we reach the end of our comprehensive exploration of Granuloma Annulare (GA), it’s clear that this journey, marked by unique challenges and advancements, is one of continuous learning and adaptation. From understanding the basics of GA to delving into the latest research and future possibilities, we have covered the multifaceted nature of this skin condition.
GA, with its varied presentations and impacts, affects the skin and touches lives profoundly. The journey of managing GA is not just about treating physical symptoms; it’s about embracing a holistic approach that includes mental well-being, lifestyle modifications, and community support.
Key Takeaways:
- Empowerment Through Knowledge: Understanding GA is the first step toward effective management. Knowledge about symptoms, triggers, and treatment options empowers people to make informed decisions about their care.
- Personalized Treatment: The evolving landscape of GA treatment, from traditional methods like corticosteroids and light therapy to emerging treatments like Tofacitinib, highlights the importance of personalized care. Future treatments promise even more tailored and effective solutions.
- Holistic Care: The management of GA extends beyond medical treatments. Lifestyle adjustments, stress management, and proper skin care are crucial in improving quality of life.
- Emotional Well-Being: Addressing the psychological impact of GA is as important as treating the physical symptoms. Seeking support, whether professional counseling or community connections, is vital.
- Hope on the Horizon: Ongoing research and clinical trials promise new insights and breakthroughs in GA treatment. The future holds potential for more targeted, effective, and personalized therapies.
In conclusion, living with Granuloma Annulare is a journey of ups and downs. Still, with the right approach, it can be navigated successfully. Continued research and advancements in treatment are paving the way for a future where GA can be managed more effectively and easily. For those affected by GA, this journey is not one they walk alone; it is a path shared with healthcare providers, researchers, and a supportive community, all moving towards a common goal of better understanding and managing this unique condition.
As we look forward, let’s carry with us the insights and knowledge gained and approach the future of GA management with optimism and hope.
FAQs: Understanding Granuloma Annulare
Granuloma Annulare (GA) often raises many questions for those affected by it and their loved ones. This FAQ section addresses some of the most common queries to provide clearer insights into this condition.
What exactly is Granuloma Annulare?
Granuloma Annulare is a skin condition described by ring-shaped lesions, usually appearing as red or skin-colored bumps. It’s a benign condition most common in children and young adults.
Is Granuloma Annulare contagious?
No, Granuloma Annulare is not contagious. It cannot be spread from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact or any other means.
What causes Granuloma Annulare?
The exact cause of GA is unknown. However, it may be linked to an overactive immune response. Other potential factors include genetic predisposition and triggers like skin injuries, certain medications, and underlying health conditions like diabetes.
How is Granuloma Annulare diagnosed?
GA is typically diagnosed through a physical skin examination and a skin biopsy. The biopsy helps rule out other conditions that may look similar to GA.
What treatment options are there for Granuloma Annulare?
GA treatment options include topical corticosteroids, corticosteroid injections, light therapy, cryotherapy, and oral medications. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and type of GA.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Granuloma Annulare?
Yes, lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy skincare routine, protecting skin from the sun, managing stress, and following a balanced diet can support the management of GA.
Will Granuloma Annulare go away on its own?
Many cases of GA resolve independently without treatment, though this can take several months to years. However, some cases may persist longer or recur.
Are there any new treatments for Granuloma Annulare?
Recent research, including studies on drugs like Tofacitinib, shows promise for new treatments. These emerging therapies focus on targeting specific pathways in the immune system.
Can Granuloma Annulare cause scars?
Typically, GA does not leave scars. However, the appearance of the skin may temporarily change due to the lesions.
Where can I find support if I have Granuloma Annulare?
Support can be found in online forums, support groups, and through healthcare providers. Connecting with others who have GA can provide emotional support and practical advice.
These FAQs offer a glimpse into the common concerns surrounding Granuloma Annulare. Consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended for more detailed information or specific medical advice.
References
- Mayo Clinic – Granuloma Annulare: Overview and treatment options.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK – Granuloma Annulare: Information on symptoms, causes, and treatment.
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – Granuloma Annulare: Detailed guide on diagnosis and management.
- Yale School of Medicine Research Study on Tofacitinib: Findings from recent research on new treatment options.
- PubMed Central: Collection of scientific studies and papers on Granuloma Annulare.