Introduction
Infectious skin conditions can cause discomfort and embarrassment and even affect our daily lives. From common conditions like impetigo and athlete’s foot to viral infections like herpes simplex, understanding and managing these conditions is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for various infectious skin conditions. Whether you’re seeking information to protect yourself or help a loved one, this article will empower you with the knowledge to navigate these conditions effectively.
Overview of Infectious Skin Conditions

Infectious skin conditions are caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that can affect the skin’s health and appearance. Therefore, understanding the different types of infectious skin conditions is essential in identifying and managing them effectively.
Bacterial Infections: One common bacterial infection is impetigo, characterized by red sores that break open and develop a yellowish-brown crust. It is highly contagious and commonly affects young children. Another bacterial infection is cellulitis, which occurs when bacteria enter the deeper layers of the skin through a cut or wound, leading to redness, warmth, and swelling.
Viral Infections: Herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes outbreaks of cold sores or genital herpes. These infections can be painful and recurring. Another viral infection is molluscum contagiosum, which presents as small, pink or flesh-colored bumps with a central indentation.
Fungal Infections: Common fungal infections include ringworm (tinea corporis), athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), and nail fungus (onychomycosis). These infections thrive in warm and moist environments and can cause itching, redness, and skin flaking.
Common Infectious Skin Conditions
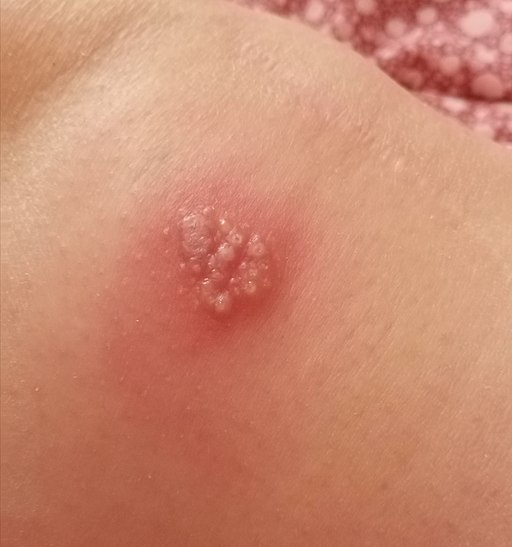
Impetigo: This contagious bacterial infection is most common in children and spreads through direct contact. It usually starts as red sores that rupture and form a honey-colored crust. Treatment involves topical or oral antibiotics and good hygiene practices to prevent its spread.
Herpes Simplex: Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) causes cold sores, while herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) causes genital herpes. Outbreaks can be triggered by stress, illness, or exposure to sunlight. Antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency and duration of outbreaks.
Ringworm (Tinea): Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by worms but by a fungus. It appears as a red, circular rash with a raised border and may cause itching. Antifungal creams or oral medications can effectively treat ringworm and prevent its spread.
Athlete’s Foot: Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection that affects the feet, causing itching, redness, and skin cracking. It commonly occurs in individuals who wear tight shoes or frequently moist environments. Antifungal creams, powders, and proper foot hygiene can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Prevention and Self-Care Practices

Preventing the spread and recurrence of infectious skin conditions is crucial. Here are some preventive measures and self-care practices to consider:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially before and after applying treatments or touching affected areas. Keep your skin clean and dry to discourage the growth of bacteria or fungi.
- Avoid skin-to-skin contact: Minimize direct contact with individuals with visible skin infections or lesions to reduce the risk of transmission. Do not share personal items like towels, clothing, or grooming tools.
- Keep the affected area clean: Cleanse it gently with mild soap and water, patting it dry afterward. Avoid scrubbing or scratching, which can worsen the condition or lead to secondary infections.
- Wear breathable clothing: Choose loose-fitting clothes made from natural fibers to allow air circulation and prevent excessive sweating, creating a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: A strong immune system can help prevent and fight infectious skin conditions. Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, sleep well, and manage stress.
Medical Treatments for Infectious Skin Conditions
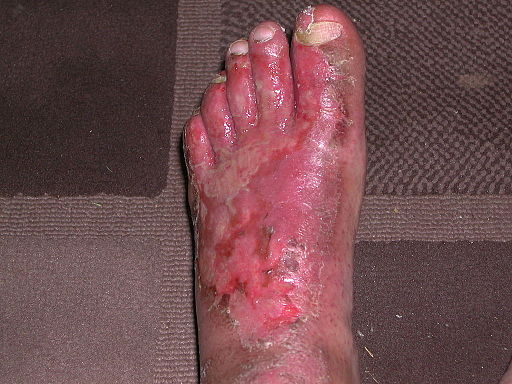
Medical treatments may be necessary when self-care measures are insufficient to manage infectious skin conditions. Here are some common medical treatment options:
Topical Medications: Depending on the type of infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe topical creams, ointments, or lotions containing antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal agents. These medications are applied directly to the affected area and help eliminate the infection.
Oral Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to treat severe or widespread infections. Antibiotics, antiviral drugs, or oral antifungal medications can effectively combat the underlying infection.
Antibiotics: Bacterial infections often require a course of oral or intravenous antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the skin infection. Taking the prescribed course of antibiotics is important to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
Antifungal Treatments: Fungal infections may require antifungal medications, such as oral antifungal tablets or topical antifungal creams. These medications help eliminate the fungus and alleviate symptoms.
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially when the infection has spread deeply or is causing complications. This may involve drainage of abscesses or debridement of infected tissue.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition. They will consider factors such as the type and severity of the infection, your medical history, and any underlying health conditions.
Natural Remedies and Home Care
Alongside medical treatments, natural remedies and home care practices can complement the management of infectious skin conditions. However, it’s essential to note that natural remedies should be used as adjunctive therapies and not replace medical treatments. Here are some options to consider:
Complementary and Alternative Therapies: Certain essential oils, such as tea tree or lavender oil, have natural antimicrobial properties and can be used topically after dilution. Aloe vera gel, known for its soothing properties, can also relieve irritated skin.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief: Applying cool compresses, taking oatmeal baths, or using over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams can help alleviate itching and inflammation associated with certain infectious skin conditions. However, following proper application guidelines is crucial and consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations: A healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support overall skin health and immune function. Include fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your diet. In addition, maintaining good overall hygiene, managing stress levels, and getting adequate sleep can promote skin health and healing.
Remember, natural remedies may vary in effectiveness and not work for everyone. Always consult a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies or home care practices, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Coping Strategies and Emotional Support
Living with infectious skin conditions can impact your emotional well-being. Here are some coping strategies and sources of emotional support:
Impact on Mental Well-being: The visible nature of certain infectious skin conditions can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, or even depression. It’s important to recognize and address the emotional impact of these conditions and seek appropriate support.
Professional Support and Counseling: Consult a dermatologist, counselor, or therapist specializing in dermatological conditions. They can provide guidance, support, and coping strategies to help manage the emotional aspects of living with infectious skin conditions.
Peer Support Groups and Online Communities: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide valuable support and understanding. Look for local support groups or join online communities where you can share experiences, learn from others, and find encouragement.
Conclusion:
Infectious skin conditions can be a source of concern and discomfort, but with proper understanding and management, you can effectively navigate these conditions. By following good hygiene practices, seeking medical treatment when necessary, and incorporating natural remedies and home care practices, you can promote healing and prevent the spread of infection.
Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can provide guidance specific to your condition and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Additionally, prioritize your emotional well-being by seeking professional support and connecting with others who can relate to your experiences. Managing the emotional impact of infectious skin conditions is an important aspect of your overall well-being.
By staying informed, practicing self-care, and seeking appropriate support, you can effectively manage infectious skin conditions and maintain healthy skin. Empower yourself with knowledge, embrace proper hygiene practices, and be proactive in seeking the necessary care to ensure optimal skin health.
FAQs
What are the common causes of infectious skin conditions?
Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause infectious skin conditions. Common causes include exposure to pathogens through direct contact, compromised immune systems, poor hygiene, or crowded environments.
How can I prevent the spread of infectious skin conditions?
Follow good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, avoiding sharing personal items, and keeping affected areas clean and covered. Minimize direct contact with individuals with visible skin infections, and seek medical treatment promptly if you suspect an infection.
Are infectious skin conditions contagious?
Many infectious skin conditions are contagious and can spread through direct contact, contaminated surfaces, or airborne transmission. It’s important to take precautions to prevent the spread of infection.
Can I treat infectious skin conditions at home?
Mild infectious skin conditions can often be managed with self-care practices, such as keeping the affected area clean, applying over-the-counter creams, or using natural remedies. However, consulting with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is crucial.
When should I seek medical attention for an infectious skin condition?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if the condition worsens, spreads rapidly, or if you experience severe symptoms such as high fever, intense pain, or difficulty functioning. Also, medical evaluation is recommended if home remedies or over-the-counter treatments don’t improve the condition within a reasonable timeframe.
Can infectious skin conditions be cured completely?
Many infectious skin conditions can be effectively managed and resolved with proper diagnosis and treatment. However, the treatment and duration may vary depending on the specific condition, individual factors, and adherence to treatment protocols.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment options.