Introduction
The prevalence of inflammatory skin conditions has increased in recent years, impacting millions worldwide. These conditions can be challenging, with many possible triggers and varying symptoms. Therefore, understanding the different types of inflammatory skin conditions, their causes, and available treatment options is crucial for anyone concerned about them. This comprehensive guide will delve into the most common inflammatory skin conditions, their triggers, and the latest research and treatments available.
Understanding Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Definition and explanation
Inflammatory skin conditions refer to a group of disorders characterized by skin inflammation. These conditions can cause redness, swelling, itching, and discomfort. The inflammation results from an overactive immune response or an abnormal immune reaction, which targets the skin and leads to various symptoms.
The Role of Inflammation in skin conditions
Inflammation is a natural defense mechanism of the body. It helps to protect against infections, injuries, and other harmful agents. However, in certain cases, the immune system can become overactive or misdirected, causing inflammation that leads to skin conditions. When inflammation occurs in the skin, it can cause redness, itchiness, and other symptoms, which can be distressing for those affected.
Common signs and symptoms
Some common signs and symptoms of inflammatory skin conditions include:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Itching
- Pain or discomfort
- Dry, scaly patches
- Blisters or pustules
- Changes in skin texture or color
The Most Common Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Psoriasis
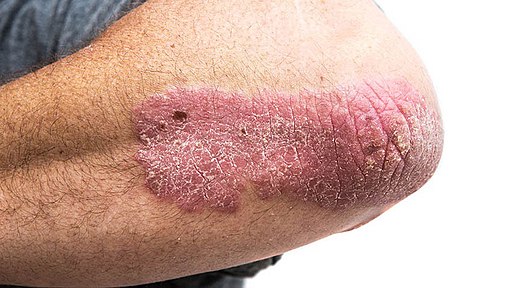
- Definition and types: Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that rapidly builds up skin cells. This accumulation leads to thick, scaly plaques on the skin’s surface. There are several types of psoriasis, including plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Symptoms and causes: Psoriasis symptoms may include red, raised patches of skin with silvery-white scales, itching or burning sensations, and cracked or bleeding skin. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it’s believed to involve genetic and environmental factors that trigger an overactive immune response.
- Treatment options: There is no cure for psoriasis, but various treatments can help manage symptoms. These include topical creams and ointments, light therapy, oral medications, and biological injections.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
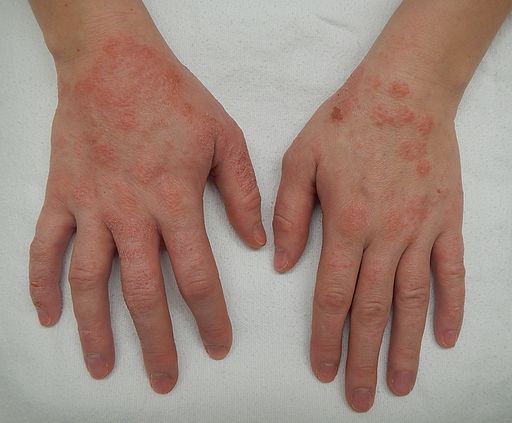
- Definition and types: Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. There are different types of eczema, including contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and nummular eczema.
- Symptoms and causes: Symptoms of eczema may include itching, redness, dryness, and oozing or crusting skin. The exact cause of eczema is poorly understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors.
- Treatment options: Eczema treatment may involve moisturizing creams, topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and other medications to control itching and inflammation. In severe cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed.
Rosacea
- Definition and types: Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition primarily affecting the face. There are four main types of

Rosacea rosacea: erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea.
- Symptoms and causes: Rosacea symptoms may include facial redness, visible blood vessels, acne-like bumps, and skin thickening. The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and vascular factors.
- Treatment options: Treatment for rosacea may include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle changes to avoid triggers such as sun exposure, spicy foods, and alcohol.
Hives (Urticaria)
- Definition and types: Hives, also known as urticaria, are a type of inflammatory skin condition characterized by raised, itchy, red welts on the skin. Hives can be classified as acute or chronic, depending on the duration of the condition.
- Symptoms and causes: Hives are typically caused by an allergic reaction to a substance, such as food, medication, or an insect bite. However, other factors, such as infections, stress, and exposure to extreme temperatures, can also cause hives.
- Treatment options: Treatment for hives usually involves oral antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling. In more severe cases, oral corticosteroids or other medications may be prescribed.
Diagnosis and Management of Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Diagnosis
- Physical examination: A healthcare provider usually begins the diagnostic process by examining the skin and asking about symptoms and medical history.
- Skin biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions or to confirm a diagnosis.
- Blood tests and allergy testing: Blood tests and allergy testing may also help identify potential causes or triggers for the skin condition.
Management and Lifestyle Modifications
- Skincare regimen: Maintaining a consistent skincare regimen, including gentle cleansing and moisturizing, can help manage and prevent symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers, such as allergens, irritants, and stress, can help minimize flare-ups.
- Sun protection: Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing can help reduce the risk of sun-induced flare-ups for some inflammatory skin conditions.
- Stress management: Engaging in stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or exercise, may help alleviate symptoms in some individuals.
Summary
Inflammatory skin conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the various types, their causes, and available treatments is essential for effectively managing these conditions. By maintaining a proper skincare regimen, avoiding triggers, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can successfully manage their symptoms and lead a more comfortable life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can inflammatory skin conditions be cured? While there is no cure for most inflammatory skin conditions, they can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications.
- What are the common triggers for inflammatory skin conditions? Common triggers may include allergens, irritants, infections, stress, and exposure to extreme temperatures.
- How can I prevent flare-ups of my inflammatory skin condition? Preventing flare-ups typically involves identifying and avoiding known triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare regimen, and seeking appropriate medical care.
