Spongiotic dermatitis is a widespread skin condition. This skin condition results in great frustration and discomfort for the patient. Most spongiotic dermatitis patients have complained about red, itchy, and inflamed skin. Studies show the disease affects everyone. The cause of this disease remains a mystery. However, medics believe it results from environmental and genetic factors. Some researchers also argue that the immune system can be one of the causal factors. Read the article for a comprehensive guide on this skin condition’s symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is Spongiotic Dermatitis?

Spongiotic dermatitis refers to a common skin condition. The skin condition involves the buildup of fluid in the epidermis. The fluid buildup causes a large swelling between your skin cells. How does the disease occur? You can see spongiotic dermatitis as itchy, flaky, and red patches. These patches resemble other types of eczema and occur on the affected skin area. The symptoms of this condition vary between patients. Medics examine the condition through biopsy and other tests. A biopsy involves taking affected skin samples for a medical examination.
Causes
The exact cause of this condition is unknown. Nonetheless, researchers link it to various environmental and genetic factors. For example, a recent study showed that a gene mutation is responsible for the disease in some patients. The mutation restricts the production of filaggrin. Thus, it weakens the skin barrier and allows moisture, allergens, and bacteria in. In addition, other factors can trigger the condition. These factors include:
- Allergens, such as dyes, plants, medication, and specific foods
- Irritants like cosmetics, latex, soaps, and some jewelry
- Increased stress levels
- Humid or dry climates
- Excessive sweating
- Severe itching
- Fungal infections
- Frequent temperature and weather conditions changes
- Hormone level changes
Risk Factors
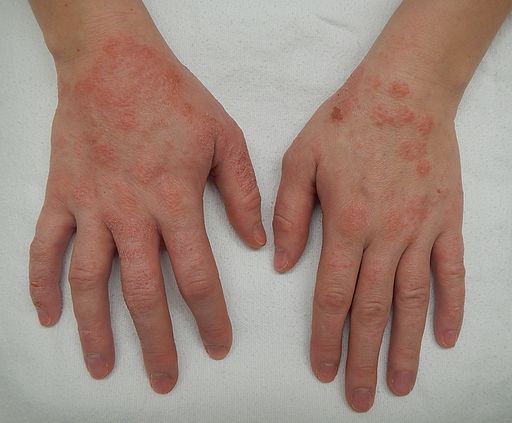
Spongiotic dermatitis has various risk factors that affect its development and severity. Below are the risk factors of this condition:
Allergies
Studies show that allergies are the common risk factor for spongiotic dermatitis. Individuals with allergies are more likely to develop these conditions. Allergic contact dermatitis, food allergies, and hay fever are common allergies. Some metals, fragrances, or medications can also cause allergies.
Irritants
Exposure to irritants can also predispose you to spongiotic dermatitis. How do irritants predispose you to this condition? These substances damage the skin and cause inflammation. Soaps, household cleaners, and some fabrics are common irritants. Environmental factors, including dry air, heat, and cold, can also trigger skin conditions.
Genetics
Genetics are also key in the development of spongiotic dermatitis. Individuals with a family history of skin conditions may be more susceptible to spongiotic dermatitis. These skin conditions range from eczema and psoriasis to allergic reactions. In addition, certain genes make an individual more likely to develop an environmental factor hypersensitivity reaction. The reaction triggers spongiotic dermatitis.
Immune system disorders
Studies show weak immune systems trigger the condition. In addition, individuals with lower immune systems increase the risk of developing spongiotic dermatitis. People with weak immune systems include those with cancer, HIV/AIDS, or chemotherapy patients. A weak immunity makes individuals susceptible to skin conditions.
Stress
Stress is one of the main risk factors. How does stress trigger this condition? Stress makes the body release hormones. These hormones trigger inflammation. In addition, the hormones exacerbate the existing skin conditions. You’ll likely get this skin condition if you have poor stress management.
Who is at the Risk of Contracting Spongiotic Dermatitis?
This skin condition can affect everyone. It can affect you regardless of age, gender, genetics, etc. Nonetheless, some individuals are usually at a greater risk. Who is at a greater risk of contracting spongiotic dermatitis? Below are the individuals at risk of this skin condition:
- Individuals prone to allergies
- Individuals in a family having a history of atopic dermatitis
- Prolonged contact with various allergens, including some medications
- Individuals working or having direct contact with metals like Nickel
- Those with a history of health complications, such as heart failure, Parkison’s disease, and HIV/AIDs.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this condition vary. They may vary depending on the severity or person. However, the symptoms start with mild itching and redness. Then, they progress to intense oozing and inflammation. Small bumps, scales, and blisters may also cover the affected area. These symptoms may interfere with daily activities, such as sleeping or working. Some patients have reported thickened or leathery skin. Why does the skin thicken? The skin thickens due to chronic inflammation and rashes.
The condition’s severity affects the symptom occurrence. For instance, mild cases cause redness and itching in a small area. More severe cases can cause widespread blistering and inflammation. Some patients may experience periodic flare-ups when having the disease. However, some individuals usually have continuous symptoms.
The affected area location can also affect the severity of the condition. For instance, the disease can be more severe on the hands or feet. Why does the condition become severe in the hands and feet? Frequent exposure to moisture or irritants worsens the disease in these parts. In addition, spongiotic dermatitis can be more severe where the skin is thinner. These body parts include the genitals or around the eyes.
Diagnose
This skin condition lacks a straightforward diagnosis. The doctor will start by physically examining the affected area of the skin. The examination involves checking for various warning signs. These signs include inflammation, itching, and skin redness. In addition, the doctor may ask you various questions about the symptoms, medical history, and medications you’re taking. The correct information will help the doctor make a diagnosis.
The physician may also perform additional tests. Additional tests help to confirm the diagnosis of spongiotic dermatitis. These tests can include a skin biopsy, patch test, and blood tests.
- A skin biopsy involves removing a small skin sample from the affected area of the skin. The doctor then examines the part under a microscope. Skin biopsy helps determine the type of dermatitis and the severity of the condition. Doctors perform the procedure under local anesthesia. You’ll receive the results in a few days.
- The patch test involves applying a small amount of the suspected allergen to the skin. The procedure helps check for the occurrence of an allergic reaction. In addition, this test helps identify the specific causal allergen. Doctors perform the procedure over several days. You can receive results within a week.
- Blood tests – help determine any underlying medical conditions triggering dermatitis. For instance, a blood test can check for lupus. Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can cause spongiotic dermatitis.
The physician may refer you to dermatologists for further examination. It usually occurs if the doctor is unsure about diagnosing spongiotic dermatitis. A dermatologist refers to a doctor who specializes in skin conditions. These specialists can perform more advanced tests. Advanced tests help to diagnose spongiotic dermatitis.
Treatment
Spongiotic dermatitis is a chronic condition that currently has no cure. However, proper management and appropriate medications can help. The treatment may vary depending on various factors. The severity of the condition and the individual patient’s needs are the main determinants. Let’s look at the different spongiotic dermatitis treatment options:
- Topical creams – Topical creams are often the first line of treatment. Patients apply these creams directly to the affected skin. Topical creams help to reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and PDE4 inhibitors are common topical creams.
- Oral medications – doctors prescribe oral medications in more severe cases. The prescription consists of antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants. You can only take oral medication for a short time. In addition, a health professional should monitor your medication closely.
- Phototherapy or light therapy – it’s a spongiotic dermatitis treatment involving UVB light. The UVB light helps reduce inflammation and itching. Light therapy applies to more severe cases. Remember to take the procedure under a health professional’s supervision.
- Use moisturizers – Spongiotic Dermatitis patients need to moisturize their skin. Moisturizing helps reduce the symptoms of spongiotic dermatitis. Experts advise that you apply these moisturizers daily and continually. Regular application helps prevent dryness and cracking of the skin.
- Avoiding Triggers – Avoiding triggers, like certain foods or environmental factors, can also help. It helps reduce the frequency and severity of spongiotic dermatitis symptoms. First, it’s good to identify the triggers of this condition. Then, keep off the triggers to control and treat the condition.
- Wet dressing – studies show the effectiveness of wet dressing in alleviating this condition. It helps to relieve itchiness and inflammation. Wet dressing involves applying a damp and cool cloth to the affected area. Keep the clothing in the area for some time.
Managing and Preventing Spongiotic Dermatitis
Besides the medical treatment, Spongiotic Dermatitis patients can adopt various preventative measures. These measures help to ease the discomfort and prevent this skin condition. Here are some of the effective measures:
- Identifying and avoiding triggers. These triggers can worsen the symptoms and severity. You can keep off certain triggers like stress and certain foods. In addition, you can avoid exposure to allergens or irritants.
- Moisturizing regularly. Ensure you use a hypoallergenic and fragrance-free moisturizer. The moisturizer will help to reduce irritation and itching.
- Use mild detergents and soaps. Studies show harsh soaps and detergents trigger this skin condition. In addition, they usually strip natural oils from the skin. Thus, this may worsen the spongiotic dermatitis symptoms. Experts advise that you consider fragrance-free and mild products.
- Wear loose-fitting and comfortable clothing.
- Practice effective stress management techniques. For example, you can try relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. These exercises help to manage stress.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. A healthy lifestyle can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Ensure you eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
- Seek support. Living with spongiotic dermatitis can be challenging. It can also impact mental health. Thus, seeking support from family, friends, or a support group will be good. This support helps you cope with the condition.
Conclusion
Spongiotic dermatitis is a common skin condition. This condition causes discomfort and inflammation. It can occur due to a variety of factors. These factors include allergies, irritants, and genetics. Spongiotic dermatitis has a wide range of symptoms. Redness, itching, and blisters or bumps are common symptoms.
Dermatologists can provide a proper diagnosis of this condition. A dermatologist may perform a physical examination and recommend skin tests or biopsies. Medical experts recommend various treatment options. The treatment includes topical creams, ointments, and oral medications. You can control the conditions by avoiding triggering factors. Proper care and management help manage the symptoms and improve their quality of life.
References
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/eczema/spongiotic-dermatitis