Bullous Pemphigoid is a fascinating yet challenging autoimmune condition that impacts people around the globe. If you or someone close to you is seeking information about this disease, you’re in the right place. This detailed guide will illuminate the reasons behind Bullous Pemphigoid, its signs, and available treatment options. Our goal is to present you with clear and precise information that empowers you to confidently manage this complex condition and make knowledgeable choices about your health.
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
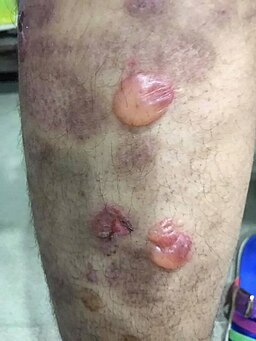
Bullous Pemphigoid is a long-term autoimmune condition where large, fluid-filled blisters, or bullae, form on the skin. These blisters can be quite itchy and cause discomfort.
Although the exact reason for Bullous Pemphigoid is unclear, scientists think it happens when the immune system wrongly attacks a protein known as BP180. This protein is critical for keeping our skin layers intact. When this protein is attacked, the top layer of the skin detaches from the lower ones, leading to bullae formation.
Bullous Pemphigoid generally affects older adults, mostly starting around the age of 70. But it’s not limited to this age group—it can affect people of any age, including children and young adults. The condition is slightly more common in women, but both genders are at risk.
Causes and Risk Factors
Even though we don’t know the exact causes of Bullous Pemphigoid, certain factors can increase the risk of developing it. For one, your genes could play a part. Studies have found that certain genetic variations might make you more likely to get the condition. Age is another important factor, as the chance of getting Bullous Pemphigoid increases as you age. Hormonal changes, particularly in women, might also contribute to the condition.
Other factors, like the environment and certain triggers, can kickstart the immune system and lead to Bullous Pemphigoid. Triggers can include exposure to some medications such as diuretics, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs. But remember, even though these medicines can be linked to Bullous Pemphigoid, they don’t necessarily cause the condition in everyone who takes them.
Signs and Symptoms

Knowing the symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid is key to catching it early and starting treatment. The main symptom is large blisters filled with fluid on the skin. These blisters have thick walls and don’t break easily. The skin around the blisters can be red and swollen. Besides the blisters, people with Bullous Pemphigoid often feel severe itching, which can greatly affect their day-to-day life.
Although the skin is the most affected area, Bullous Pemphigoid can also affect other areas covered by a mucous membrane like the mouth and throat. This can cause discomfort and make it hard to eat or speak. Sometimes, the condition can affect the eyes, leading to conjunctivitis or other eye problems. People with Bullous Pemphigoid may also see changes in their nails, such as ridges or small dents, known as pitting.
Diagnosing Bullous Pemphigoid

Spotting Bullous Pemphigoid early is key to managing it effectively. Doctors use a mix of your medical history, physical exams, and tests to confirm whether you have Bullous Pemphigoid and rule out other similar conditions.
Your doctor will first ask about your symptoms, your medical history, and any medications you’re taking. After this, they’ll perform a thorough physical exam, paying close attention to your skin and mucous membranes. Then, they’ll take a small sample of your skin, or a biopsy, from an affected area. This sample will be studied under a microscope to look for changes that point to Bullous Pemphigoid. Blood tests and immune system studies may also be done to find specific antibodies linked to the condition and to distinguish it from other autoimmune disorders.
Treatment Options
When treating Bullous Pemphigoid, the main goal is to manage symptoms, help existing blisters heal, and stop new ones from forming. Treatment strategies can vary based on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors.
Topical treatments like corticosteroid creams or ointments are usually the first line of defense for mild to moderate cases of Bullous Pemphigoid. These treatments help soothe inflammation and itching. For more serious cases, systemic medications, such as oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, might be needed to control the immune response and manage the condition. However, it’s crucial to note that these medications can have side effects. Hence, regular check-ins with healthcare professionals are vital.
Lifestyle Management and Self-Care
Along with medical treatment, self-care is crucial in managing Bullous Pemphigoid and enhancing overall well-being. Here are some useful tips to help you care for your skin and alleviate symptoms:
- Keep your skin clean and moisturized using gentle, fragrance-free products.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing affected areas to prevent further damage.
- Choose to wear loose, comfy clothes made of soft materials.
- Keep your skin safe from too much sun exposure by using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
- Follow a healthy diet that’s packed with nutrients to give your immune system a boost.
- Use relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga to manage stress levels.
- Don’t hesitate to seek emotional and psychological support from friends, family, or support groups.
Promising Research and Future Directions
Scientists worldwide are working hard to improve our understanding of Bullous Pemphigoid and develop new treatment methods. Exciting research is being done on targeted immunotherapies, new methods of wound healing, and potential markers for early detection and tracking of the disease. While there’s still a lot to learn, these efforts offer hope for better management and results for people living with Bullous Pemphigoid.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Bullous Pemphigoid can cause more than just physical discomfort – it can also lead to other complications. Chronic inflammation and long-term use of certain medicines can impact your body. Here are a few potential complications:
- Infections: Due to skin damage, people with Bullous Pemphigoid have a higher risk of skin infections, such as cellulitis.
- Scarring: Once the bullae heal, they might leave behind scars. These can be uncomfortable and affect movement, especially if they are near joints or flexing areas.
- Secondary Injuries: Severe itching and discomfort can lead to scratching or rubbing, leading to further injuries and infections.
- Reduced Quality of Life: The physical symptoms and emotional stress of Bullous Pemphigoid can affect daily activities, sleep, and overall well-being, leading to a reduced quality of life.
That’s why doctors need to closely monitor these potential complications, to manage them early and lessen their impact on people with Bullous Pemphigoid.
Managing Bullous Pemphigoid During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can bring extra challenges for people with Bullous Pemphigoid. It’s important to consider how medicines might affect the mother and the growing baby. Here are some points to consider:
- Weighing the Risks and Benefits of Medication: Healthcare providers will look at the risks and benefits of using medicines for Bullous Pemphigoid during pregnancy. They might adjust or stop some medicines to lower possible risks to the baby.
- Regular Check-ups: If you’re pregnant and have Bullous Pemphigoid, you’ll need to see your healthcare provider more often. They’ll closely monitor your and your baby’s health, which might involve more regular tests.
- Teamwork and Communication: Open and regular chats between you, your skin doctor (dermatologist), and your pregnancy doctor (obstetrician) are key. Working together, they’ll create a plan that suits you best, aiming for the best possible outcome for you and your baby.
Tips for Caregivers and Loved Ones
Supporting someone with Bullous Pemphigoid takes understanding and kindness. Here are some tips for caregivers and loved ones:
- Learn About the Condition: Try to understand Bullous Pemphigoid by learning about it. Knowing about the symptoms and how they affect daily life will help you offer the right support and care.
- Give Practical Help: You can lend a hand with daily tasks that might be tough for someone with Bullous Pemphigoid. This could include helping with bathing, getting dressed, or making meals. You could also offer to go with them to doctor’s appointments or give them a ride if needed.
- Offer Emotional Support: Bullous Pemphigoid can take an emotional toll. Be there to listen, be patient, and understand. Give reassurance and encouragement when times are tough.
- Promote Self-Care: Encourage good self-care habits. This could include sticking to treatment plans, living a healthy lifestyle, and doing things to reduce stress. If they’re interested, suggest joining a support group or seeking counseling.
And don’t forget about yourself. Caregivers need support too. Look for support groups or counseling services to help with your emotional needs and keep yourself well.
Coping with Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with Bullous Pemphigoid can impact your emotions and mental health. Here’s how you can manage these challenges:
- Find a Support Network: Joining support groups or online communities can help. Here, you can share your experiences, get advice, and connect with others going through similar struggles.
- Manage Stress: Try activities that reduce stress. This could include deep breathing exercises, meditation, mindfulness, or hobbies you enjoy and help you relax.
- Get Professional Help: If you’re dealing with anxiety, depression, or overwhelming stress, consider seeking help from a therapist or counselor. Look for those who specialize in dealing with chronic illnesses or skin-related issues.
- Communicate Openly: Share your feelings and worries with people you trust, like friends, family, or healthcare providers. This can help lighten your load and provide some relief.
Remember, looking after your mental health is crucial to managing Bullous Pemphigoid. By dealing with the emotional impacts, you can build resilience and improve your overall quality of life.
Conclusion
To sum up, Bullous Pemphigoid is a complex autoimmune condition that can greatly impact those living with it. But, by learning about its causes, spotting the symptoms, and understanding the treatment options, you can take active steps to manage this condition effectively. It’s always important to seek advice from healthcare professionals for the right diagnosis, treatment plans tailored to your needs, and continuous support. Armed with the right information and resources, you can confidently and positively manage your journey with Bullous Pemphigoid.
FAQs
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about Bullous Pemphigoid:
Is Bullous Pemphigoid contagious?
No, Bullous Pemphigoid isn’t contagious. It’s an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s skin cells.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid be cured?
While there’s no known cure for Bullous Pemphigoid, it can be effectively managed with the right medical treatments. Treatment aims to control symptoms, help to heal and prevent flare-ups.
Does stress make Bullous Pemphigoid worse?
Stress can potentially trigger or worsen symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid in some people. That’s why managing stress and seeking support to handle it is important.
Are there any dietary restrictions for people with Bullous Pemphigoid?
There aren’t any specific foods that people with Bullous Pemphigoid should avoid. However, a balanced diet is important for overall health and supporting the immune system. It’s best to consult with a healthcare professional or dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid affect organs other than the skin?
While the major impact of Bullous Pemphigoid is on the skin, it can sometimes affect other mucous membranes, like the mouth and eyes. It’s rare for it to affect other organs.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid go into remission?
Yes, Bullous Pemphigoid can go into remission, where symptoms ease or disappear. This can be achieved with the right medical treatment. Still, it’s important to keep monitoring the condition and follow the treatment plan recommended by healthcare providers.
Are there alternative or complementary therapies for Bullous Pemphigoid?
While alternative and complementary therapies can be considered, consulting with healthcare providers before trying additional treatments is important. These therapies should be used to support overall well-being and not as a replacement for medical treatments.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid affect children or younger adults?
Although Bullous Pemphigoid typically affects older adults, it can occur at any age, including in children and younger adults. The approach to management and treatment may differ based on the person’s age.
Will Bullous Pemphigoid resolve on its own without treatment?
Bullous Pemphigoid rarely resolves on its own without treatment. It’s important to seek medical help for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to avoid complications and manage symptoms effectively.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid relapse after treatment?
Bullous Pemphigoid can have periods of relapse and remission. Regular monitoring and sticking to the treatment plan are crucial to managing the condition and minimizing relapses’ severity and frequency.
Remember, these answers are general guidelines. It’s always best to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations based on your unique situation.
References
- NHS – Bullous Pemphigoid
- Mayo Clinic – Bullous Pemphigoid
- DermNet NZ – Bullous Pemphigoid by Prof. Amanda Oakley
- National Institutes of Health – Bullous Pemphigoid by Dana Baigrie and Vinod Nookala
- American Academy of Dermatology – Bullous Pemphigoid: Signs and symptoms
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and guidance regarding Bullous Pemphigoid or any other medical condition. The author and the website shall not be held responsible for any potential consequences arising from using or applying the information presented in this article.