Ah, the great outdoors. There’s nothing like a breath of fresh air, right? As invigorating as it may be, the environment can sometimes be less than friendly to our skin. Various environmental factors can lead to many skin conditions, from the beaming sun to the bitter cold. You’re in the right place if you’ve ever wondered how the weather and climate affect your skin. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of environmental skin conditions, their causes, symptoms, and how you can protect your skin. So, let’s get started, shall we?
What are Environmental Skin Conditions?
Before we venture any further, let’s clarify what we mean by ‘environmental skin conditions.’ Simply put, these are skin problems that arise due to your environment’s influence. This could be anything from the climate and weather conditions you live into the air quality in your area. You see, our skin is a bit of a superhero, acting as a shield against external threats. But even superheroes have their kryptonite, and for skin, these include harmful UV rays, extreme temperatures, and pollution, to name a few.
The Impact of Different Environmental Factors on Skin

Our environment can impact our skin in various ways, both good and bad. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key environmental factors that can affect skin health:
- Sun Exposure: The sun, while vital for vitamin D synthesis, is a bit of a double-edged sword when it comes to skin health. Overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation can lead to sunburn, premature skin aging, and even skin cancer.
- Cold Weather: Ever noticed your skin becoming dry and flaky during winter? Cold, dry air can strip the skin of its natural moisture, leading to dryness, redness, and even frostbite in extreme cases.
- Heat and Humidity: On the flip side, hot and humid conditions can make your skin sweat excessively, leading to conditions like heat rash and exacerbating acne and other skin infections.
- Air Pollution: Air pollutants can penetrate the skin, causing oxidative stress that accelerates skin aging and can trigger inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Wind Exposure: Wind can be harsh on the skin, leading to windburn and dryness, especially in colder climates.
- High Altitudes: High-altitude environments can be harsh on the skin due to increased UV exposure and low humidity, leading to dryness and increased risk of sunburn.
Understanding these factors is the first step towards better skin health. Now let’s explore some specific environmental skin conditions in more detail.
In-Depth Look at Specific Environmental Skin Conditions

Now, let’s delve deeper into some specific environmental skin conditions.
1. Sunburn
Sunburn happens when the skin gets damaged from the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. It’s like nature’s way of saying, “You’ve had too much sun for today.”
Symptoms: Red, painful, and warm skin that later peels off. In severe cases, you may experience blisters, fever, and chills.
Treatment: Cooling the skin with a damp cloth, applying aloe vera or over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream can help. But remember, prevention is always better than cure, so slap on that SPF!
2. Melasma
Also known as ‘the mask of pregnancy,’ melasma is a common skin problem causing brown patches on the face. It’s more like an unwanted souvenir of hormonal changes during pregnancy or from sun exposure.
Symptoms: Brown or grayish-brown patches usually appear on the face, especially on the cheeks, bridge of the nose, forehead, and above the upper lip.
Treatment: Sun protection and lightening creams can help. Dermatologists may also suggest procedures like chemical peels, dermabrasion, or laser treatment.
3. Actinic Keratosis
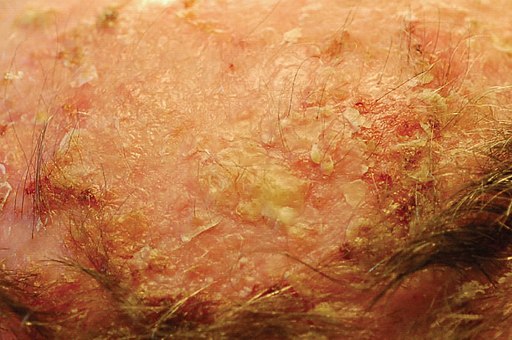
This condition is caused by long-term sun or tanning bed exposure. It’s a rough, scaly patch on your skin that develops slowly over years.
Symptoms: Dry, rough, slightly raised patches or bumps, usually on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, neck, hands, and forearms.
Treatment: Removal methods like cryotherapy (freezing), topical creams, or photodynamic therapy are often used.
4. Contact Dermatitis
This one is triggered when the skin comes into contact with a substance that it doesn’t quite agree with. This could be anything from poison ivy to certain soaps and detergents.
Symptoms: Red rash, itching, dry, cracked, or scaly skin. In severe cases, blisters and burns can occur.
Treatment: Avoiding the irritant, using mild soaps, and applying anti-itch creams can help manage symptoms.
5. Rosacea
Rosacea is a common skin condition often triggered by environmental factors like sun exposure, hot weather, wind, and cold.
Symptoms: Facial redness, swollen red bumps, and visible blood vessels. It often flares up for a few weeks to a few months and then diminishes for a while.
Treatment: While there’s no cure for rosacea, treatments can control and reduce the signs and symptoms. These include topical drugs, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle changes.
These are just a few examples of how the environment can impact our skin. Remember, if you notice any unusual changes in your skin, it’s always best to consult a dermatologist. Now, let’s look at how these conditions are diagnosed and treated.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Environmental Skin Conditions

If you’re facing any skin troubles, don’t just sit there and Google your symptoms. It’s essential to get a professional diagnosis. Dermatologists use various methods to diagnose skin conditions. This could involve a physical exam, where they examine your skin and may even use a special lamp to look at it more closely. In some cases, they might take a small sample (biopsy) for testing.
Once diagnosed, the treatment varies depending on the type of skin condition. This could range from topical creams and oral medication to more advanced treatments like laser therapy. Don’t be disheartened if the first line of treatment doesn’t work instantly. Sometimes it takes a bit of trial and error to find what works best for your skin.
Preventive Measures and Protection Strategies
As the old saying goes, “Prevention is better than cure.” Here are some strategies you can adopt to protect your skin from environmental factors:
- Sun Protection: Apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days. Wear protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat when out in the sun.
- Cold Weather Protection: Keep your skin moisturized to combat dryness. Wear layers to protect your skin from the cold, and don’t forget your gloves and scarf!
- Heat and Humidity Protection: Stay hydrated and cool. Use oil-free skin products to prevent clogged pores and heat rashes.
- Air Pollution Protection: Cleanse your skin thoroughly at the end of the day to remove pollutants. Antioxidant-rich skincare products can help fight off free radicals caused by pollution.
- Wind Protection: Protect your skin with scarves and hats in windy weather. Using a thicker moisturizer can also help prevent dryness.
- High Altitude Protection: At high altitudes, UV radiation is stronger, and the air can be dry. So, don’t skimp on sunscreen and moisturizer.
While these strategies can help, it’s also crucial to adopt a skin-friendly lifestyle.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Skin Health

Taking care of your skin isn’t just about what you put on it; it’s also about what you put in your body and how you live your life. Here are some lifestyle changes that can promote better skin health:
1. Nutrition: What you eat can have a big impact on your skin. Fill your plate with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in antioxidants can help fight damage from environmental factors.
2. Hydration: Drinking enough water keeps your skin hydrated from within. If you’re in a hot climate or exercising, you may need to drink more to replace the fluids you lose through sweat.
3. Exercise: Regular exercise can increase blood flow, which helps nourish skin cells and keep them vital. Just remember to cleanse your skin after a workout to remove sweat and bacteria.
4. Stress Management: High-stress levels can worsen some skin conditions like psoriasis and rosacea. Find stress-reducing activities you enjoy, like reading, yoga, or gardening.
FAQs
To wrap up, let’s tackle some frequently asked questions about environmental skin conditions:
Can environmental skin conditions be cured?
While some conditions can be resolved with treatment, others, like rosacea and eczema, can’t be cured but can be managed effectively with the right treatment plan and lifestyle changes.
How can I protect my skin from pollution?
Keeping your skin clean, using antioxidant-rich skincare products, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help protect your skin from pollution.
Can sun exposure cause skin conditions?
Yes, excessive sun exposure can lead to skin conditions like sunburn, actinic keratosis, and even skin cancer.
How does cold weather affect my skin?
Cold, dry air can strip the skin of its natural moisture, leading to dryness, redness, and even frostbite in extreme cases.
Does climate change affect my skin?
Yes, changes in the climate can impact your skin. Increased temperatures can lead to increased sweating and oil production, which can exacerbate conditions like acne. On the other hand, colder temperatures and lower humidity levels can dry out your skin, leading to conditions like eczema.
Are there any natural remedies for environmental skin conditions?
Yes, there are natural remedies that can help soothe and manage some environmental skin conditions. For instance, aloe vera can soothe sunburn, while oatmeal baths can help with eczema flare-ups. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
Can diet impact my skin’s reaction to environmental factors?
Absolutely. A diet rich in antioxidants can help your skin fight off damage from environmental factors like UV rays and pollution. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and flaxseeds, can also help keep your skin hydrated and healthy.
How often should I apply sunscreen when I’m outside?
You should apply sunscreen every two hours when you’re outside, even if it’s cloudy. If you’re swimming or sweating heavily, you’ll need to reapply more frequently. Don’t forget to apply it to all exposed skin, including often-missed spots like the ears and back of the neck.
Is all skin equally affected by environmental factors?
No, different skin types can react differently to environmental factors. For example, fair skin is more susceptible to sunburn, while oily skin may be more prone to acne in hot, humid conditions. It’s important to understand your skin type and tailor your skincare routine accordingly.
Can I develop a new environmental skin condition later in life?
Yes, it’s possible to develop new skin conditions at any age, depending on various factors, including changes in your environment, lifestyle, or overall health. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can help detect and manage any new conditions early.
Conclusion
The environment can have a significant impact on our skin, but with the right knowledge and care, we can keep our skin healthy and glowing, come rain or shine. So, whether you’re hitting the beach or braving the winter chill, remember to protect your skin. After all, it’s the only one you’ve got!
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this article.