Ringworm vs. Eczema- what is the difference?
Eczema and Ringworm are two different skin disorders that are often confused. They have many similar symptoms, making it difficult to differentiate between them, especially if you don’t know much about them. But although these two skin conditions share some symptoms, they have distinct differences. So, if you have not been able to tell the difference between ringworms and Eczema, you have come to the right place. In this guide, we will review these two skin conditions in detail to help you know what they are, their signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and, most importantly, how they differ. Make sure you read until the end so that you don’t miss any crucial piece of information. Now, for any further delay, let’s dive into the article.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Definition
• Ringworm

Dermatophytosis, another name for Ringworm, is a common fungal infection resulting in a ring-shaped skin infection. Contrary to its name, worms do not cause Ringworm. Instead, the fungus causes it.
At the initial stage, the affected area usually appears discolored and with scaly patches that are brown-gray on darker skin and red on lighter skin. This skin condition affects animals and humans and can quickly spread from one part of the body to another if you don’t treat it on time. That is why we recommend treating this condition immediately when you identify it.
Common areas where ringworms are likely to attack include nails, hands, feet, beards, and scalp. It is also important to note that ringworms are named differently depending on where they attack. For instance, if ringworms attack your feet, it is known as Tinea Pedis, and if it affects your face, it’s Tinea faciei. Ringworms usually cause itchiness and loss of hair in the areas they attack. Symptoms of ringworms squally appear on the skin faster than on the scalp.
• Eczema
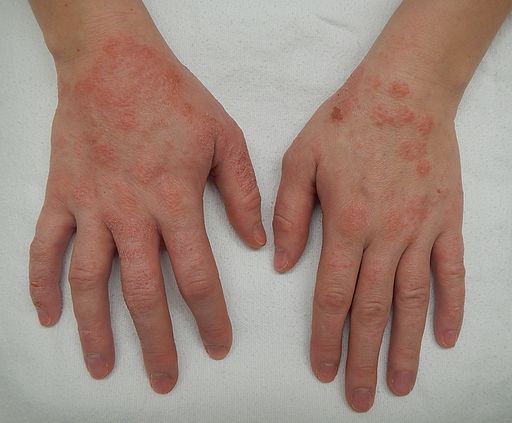
Eczema, often known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that causes itchy, red, and inflamed patches on the skin. It’s not contagious, and it can occur at any age.
“Atopic” refers to a group of allergic conditions that are often inherited, such as asthma, allergic rhinitis (hay fever), and atopic dermatitis (Eczema). People with atopic conditions tend to develop allergic reactions to normally harmless substances, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. This is because their immune system reacts to these substances as if they were harmful, triggering an allergic response. Eczema, called Atopic dermatitis, is commonly associated with atopic conditions.
Eczema is very common in infants. Statistics show that this skin condition affects up to 20% of infants and about 3% of adults in the United States. Unfortunately, this skin condition has no cure. Some people usually experience the symptoms of Eczema on and off for their entire life, but some usually outgrow it over time. However, Eczema can easily be managed by following the right treatment and avoiding triggers.
Another important thing to note about Eczema is that it is not contagious, meaning you cannot spread it to another person, as with ringworms. Common Eczema triggers include food such as dairy products and nuts and environmental factors such as pollen grains, smoke, and fragrances.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Symptoms
One of the reasons why many people find it difficult to differentiate between these two skin conditions is because they share many symptoms. In this section, we will discuss the symptoms of these two skin conditions to help you know the symptoms they share and those they don’t.
Ringworms
Common signs and symptoms of ringworms include:
- A scaly or clear area with the appearance of pumps that changes in color from grey or brown on black skin or red on light skin.
- Itchiness
- A scaly ring-shaped area, mostly on the legs, arms, or buttocks.
- Overlapping rings
- Slightly raised rings that keep expanding
- Hair loss
It is important to remember that ringworms typically have a different appearance depending on the area of the body they have affected. For instance, if it attacks your body, the Ringworm will appear as patches with a round ring shape. On the other hand, if it attacks the scalp, then bald patches caused by hair loss may appear.
Symptoms of Eczema
Common symptoms of Eczema include:
- Swelling
- Very Dry skin
- Bumps on the skin
- Itchy skin
- Thick patches on the skin
- Rashes on the skin
- Skin infections
- Bumps on the skin
- Weeping, crushed, or sometimes open sores
People with severe Eczema need special treatment and care to relieve those symptoms. If not, they may continue to scratch and rub the area causing skin infections. Eczema symptoms are usually harder to detect for people of color because the rashes are usually brown or gray. The most typical form of Eczema is atopic dermatitis, affecting nearly 20% of babies in the United States.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Causes
Causes of Ringworm:
Ringworm is a contagious fungal disease caused by mold-like parasites on the outer layer of your skin cells. As mentioned earlier, this skin condition affects both animals and humans.
It can spread in multiple ways, including via human to human through skin contact, animal to human through contact with the infected part of the animal skin, soil to human through contact with the infected soil and object to human through an infected object. Ringworm does not have triggers. You will only get this skin infection if you have a fungal infection.
Causes of Eczema:
Unlike Ringworm, whose cause is clear, the cause of Eczema to date remains unclear. However, doctors believe that environmental and genetic factors cause Eczema. Additionally, certain things such as some metals, fragrances, soap, dry skin, fabrics like polyester or wool, smoking cigarettes, and using antibacterial ointments can also cause this skin condition.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Diagnosis
Ringworm
When you visit your physician, he/she will examine your skin using a black light to determine whether you suffer from Ringworm. If the doctor detects signs of Ringworm via this procedure, he will request that you conduct additional tests to ascertain that you are indeed suffering from Ringworm. These tests include:
- A fungal culture or skin biopsy: This process includes taking a sample of your skin or a discharge from your skin and then sending it to the laboratory for further examination to detect if there is the presence of fungus and the type of fungus that has caused the infection.
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) examination- This test includes scraping off a small area of the affected skin and then adding drops of potassium hydroxide to it. Potassium hydroxide will break the skin cells, making it easier to detect fungal elements under the microscope.
Eczema
Most professional healthcare providers can easily detect whether you have Eczema or not just by examining your skin closely. This is because Eczema’s appearance is distinct and easy to detect.
Additionally, this skin condition is very common amongst infants, thus, quite easy to detect. But because Eczema shares many symptoms with other skin conditions like Ringworm, the doctor will conduct further tests to confirm that you are indeed suffering from Eczema.
These tests include A skin biopsy to determine the type of Eczema the patient is suffering from, a blood test to check for rushes unrelated to this skin condition, and an allergy test.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Treatment
Although these two skin conditions have many things in common, their causes are different, meaning their treatment is also different. Therefore, it is important to correctly diagnose these two skin conditions because one treatment will not work for the other.
• Ringworm treatment
As mentioned earlier, Ringworm is a skin condition caused by a fungus infection. As a result, the doctor may recommend lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter medications.
The medication the doctor will recommend will depend on the type of Ringworm the patient is suffering from and the severity of the condition. Mild Ringworm is usually treated with antifungal sprays, gels, creams, and ointments, while severe cases are usually treated with oral medications such as Terbinafine.
The doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes like observing proper hygiene like washing your bedding regularly, drying your skin thoroughly after bath, and much more.
• Eczema treatment
First, it is important to note that Eczema has no cure. However, several treatments can help to manage this skin condition. Eczema is a general term that represents a group of skin conditions. This means that the physician’s treatment will depend on the type and cause of this skin condition.
Also, unlike Ringworm, caused by a fungus, Eczema does not have a known cause. As a result, the treatment that the doctor prescribes will depend on the cause. For instance, if the doctor establishes that the cause of Eczema is an allergy, then he/she will prescribe an anti-allergic medication like antihistamines.
Other treatments for Eczema include the use of oral medications like immunosuppressants, topical corticosteroid ointments, and creams that are applied directly to the skin, antibiotics to treat skin infection, barrier repair moisturizers to help repair skin damage, topical calcineurin inhibitors that prevent flares as well as reduce inflammation and phototherapy.
Ringworm vs. Eczema: Differences
Now that you know what these two skin conditions are, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment, let’s look at how they differ. Ringworm and Eczema have many similarities regarding signs and symptoms, which is why many people find it difficult to differentiate between them. However, they also have quite several distinct differences, as discussed below.
Cause Difference
One of the biggest differences between these two skin conditions is their causes. A fungal infection causes Ringworm, and it is quite easy to treat this skin condition. Eczema, on the other hand, does not have known causes. Doctors believe many factors cause it, including genetics, environmental factors, food, etc. The fact that it does not have a known cause makes it quite difficult to treat.
How they spread
Another major difference between these two skin conditions is how they spread. For example, Ringworm is a highly contagious skin condition transmitted through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, object, or animal. Ringworm can quickly spread to different body parts if not treated on time. On the other hand, Eczema is not contagious, meaning you cannot spread it to another person even if you make skin contact.
Treatment
Ringworm and Eczema also differ in how they are treated. Since the cause of Ringworm is well known, this skin condition can easily be treated using over-the-counter antifungal medications. The doctor can prescribe Topical or oral medication depending on the severity of the problem. On the other hand, Eczema does not have a known cause and thus does not have a specific treatment option.
The type of treatment the doctor administers depends on the patient’s symptoms. For instance, if an allergy causes the condition, the doctor will prescribe anti-allergy medication. The type of treatment the doctor administers depends on the patient’s symptoms.
How they appear
The appearance of these two skin diseases also differs greatly. Ringworms are usually round with black dots at the center. Ringworm is also very itchy. Conversely, Eczema usually causes swelling, redness, and sometimes oozing on the affected area.
How long do they last
The last difference between these two skin conditions is how long they last. As mentioned, Eczema has no cure, and in most cases, it usually goes and comes depending on how it is managed. Some patients can outgrow the symptoms of Eczema, but in most cases, this skin condition often lasts for a lifetime. On the other hand, ringworms have an available medication and can thus be treated once diagnosed.
Conclusion
Ringworm and Eczema are two skin conditions with similar symptoms but different. Ringworm is a fungal infection that causes a ring-shaped rash, while Eczema is a skin condition that causes itchy, red, and inflamed patches on the skin.
Eczema is not contagious and is associated with atopic conditions, while Ringworm can cause hair loss and is contagious. You can manage both conditions with proper treatment and by avoiding triggers.
It’s important to know the differences between the two to receive appropriate treatment, and if you need more clarification, it’s best to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis.